Redox Homeostasis in Thyroid Cancer: Implications in Na+/I- Symporter (NIS) Regulation
- PMID: 35682803
- PMCID: PMC9181215
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116129
Redox Homeostasis in Thyroid Cancer: Implications in Na+/I- Symporter (NIS) Regulation
Abstract
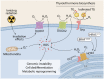
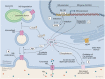
Radioiodine therapy (RAI) is a standard and effective therapeutic approach for differentiated thyroid cancers (DTCs) based on the unique capacity for iodide uptake and accumulation of the thyroid gland through the Na+/I- symporter (NIS). However, around 5-15% of DTC patients may become refractory to radioiodine, which is associated with a worse prognosis. The loss of RAI avidity due to thyroid cancers is attributed to cell dedifferentiation, resulting in NIS repression by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. Targeting the signaling pathways potentially involved in this process to induce de novo iodide uptake in refractory tumors is the rationale of "redifferentiation strategies". Oxidative stress (OS) results from the imbalance between ROS production and depuration that favors a pro-oxidative environment, resulting from increased ROS production, decreased antioxidant defenses, or both. NIS expression and function are regulated by the cellular redox state in cancer and non-cancer contexts. In addition, OS has been implicated in thyroid tumorigenesis and thyroid cancer cell dedifferentiation. Here, we review the main aspects of redox homeostasis in thyrocytes and discuss potential ROS-dependent mechanisms involved in NIS repression in thyroid cancer.
Keywords: NIS; radioiodine therapy; reactive oxygen species; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Durante C., Haddy N., Baudin E., Leboulleux S., Hartl D., Travagli J.P., Caillou B., Ricard M., Lumbroso J.D., De Vathaire F., et al. Long-Term Outcome of 444 Patients with Distant Metastases from Papillary and Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma: Benefits and Limits of Radioiodine Therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006;91:2892–2899. doi: 10.1210/jc.2005-2838. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

