A Review on the Role of Bicarbonate and Proton Transporters during Sperm Capacitation in Mammals
- PMID: 35683013
- PMCID: PMC9180951
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116333
A Review on the Role of Bicarbonate and Proton Transporters during Sperm Capacitation in Mammals
Abstract
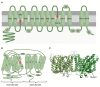
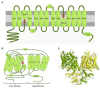
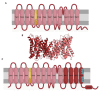
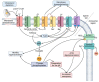
Alkalinization of sperm cytosol is essential for plasma membrane hyperpolarization, hyperactivation of motility, and acrosomal exocytosis during sperm capacitation in mammals. The plasma membrane of sperm cells contains different ion channels implicated in the increase of internal pH (pHi) by favoring either bicarbonate entrance or proton efflux. Bicarbonate transporters belong to the solute carrier families 4 (SLC4) and 26 (SLC26) and are currently grouped into Na+/HCO3- transporters and Cl-/HCO3- exchangers. Na+/HCO3- transporters are reported to be essential for the initial and fast entrance of HCO3- that triggers sperm capacitation, whereas Cl-/HCO3- exchangers are responsible for the sustained HCO3- entrance which orchestrates the sequence of changes associated with sperm capacitation. Proton efflux is required for the fast alkalinization of capacitated sperm cells and the activation of pH-dependent proteins; according to the species, this transport can be mediated by Na+/H+ exchangers (NHE) belonging to the SLC9 family and/or voltage-gated proton channels (HVCN1). Herein, we discuss the involvement of each of these channels in sperm capacitation and the acrosome reaction.
Keywords: HVCN1 channels; NHE; SLC26 channels; SLC4 channels; mammals; sperm capacitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AGL2017-88329-R/Ministry of Science and Innovation, Spain
- PRE2018-083488/Ministry of Science and Innovation, Spain
- PID2020-113320RB-I00/Ministry of Science and Innovation, Spain
- 2017-SGR-1229/Catalan Agency for Management of University and Research Grants, Regional Government of Catalonia, Spain
- ICREA/Catalan Institution for Research and Advanced Studies
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

