Bio-Synthesis of Aspergillus terreus Mediated Gold Nanoparticle: Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Antifungal and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
- PMID: 35683175
- PMCID: PMC9181662
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15113877
Bio-Synthesis of Aspergillus terreus Mediated Gold Nanoparticle: Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Antifungal and In Vitro Cytotoxicity Studies
Abstract
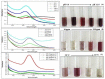
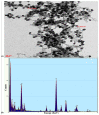
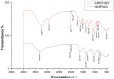
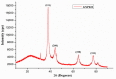
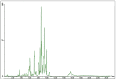
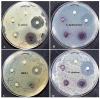
Gold nanoparticles (GNP) were bio-fabricated utilizing the methanolic extract of the endophytic isolate Aspergillus terreus. The biosynthesised gold nanoparticles (GNP023) were characterised using UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis); transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier-transform nfrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. The bio-fabricated GNP023 displayed a sharp SPR peak at 536 nm, were spherically shaped, and had an average size between 10-16 nm. The EDX profile confirmed the presence of gold (Au), and XRD analysis confirmed the crystalline nature of GNP023. The antimicrobial activity of GNP023 was investigated against several food-borne and phytopathogens, using in vitro antibacterial and antifungal assays. The maximum zone of inhibition was observed for S. aureus and V. cholera at 400 μg /mL, whereas inhibition in radial mycelial growth was observed against Fusarium oxysporum and Rhizoctonia solani at 52.5% and 65.46%, respectively, when challenged with GNP023 (200 μg/mL). Moreover, the gold nanoparticles displayed significant antioxidant activity against the ABTS radical, with an IC50 of 38.61 µg/mL, and were non-toxic when tested against human kidney embryonic 293 (HEK293) cells. Thus, the current work supports the application of myco-synthesised gold nanoparticles as a versatile antimicrobial candidate against food-borne pathogens.
Keywords: Aspergillus sp.; antibacterial; antifungal; endophytic fungi; gold nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Elegbede J.A., Lateef A., Azeez M.A., Asafa T.B., Yekeen T.A., Oladipo I.C., Aina D.A., Beukes L.S., Gueguim-Kana E.B. Biofabrication of gold nanoparticles using xylanases through valorization of corncob by Aspergillus niger and Trichoderma longibrachiatum: Antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticoagulant and thrombolytic activities. Waste Biomass Valorization. 2020;11:781–791. doi: 10.1007/s12649-018-0540-2. - DOI
-
- Ojo S.A., Lateef A., Azeez M.A., Oladejo S.M., Akinwale A.S., Asafa T.B., Yekeen T.A., Akinboro A., Oladipo I.C., Gueguim-Kana E.B., et al. Biomedical and catalytic applications of gold and silver-gold alloy nanoparticles biosynthesized using cell-free extract of Bacillus safensis LAU 13: Antifungal, dye degradation, anti-coagulant and thrombolytic activities. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 2016;15:433–442. doi: 10.1109/TNB.2016.2559161. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sharma R., Singh D., Singh R. Biological control of postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetables by microbial antagonists: A review. Biol. Control. 2009;50:205–221. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2009.05.001. - DOI
-
- Eng S.-K., Pusparajah P., Mutalib N.-S.A., Ser H.-L., Chan K.-G., Lee L.-H. Salmonella: A review on pathogenesis, epidemiology and antibiotic resistance. Front. Life Sci. 2015;8:284–293. doi: 10.1080/21553769.2015.1051243. - DOI
-
- Välimaa A.-L., Tilsala-Timisjärvi A., Virtanen E. Rapid detection and identification methods for Listeria monocytogenes in the food chain—A review. Food Control. 2015;55:103–114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2015.02.037. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

