Significant Decrease in the Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression after Hepatitis C Eradication
- PMID: 35683432
- PMCID: PMC9181745
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11113044
Significant Decrease in the Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression after Hepatitis C Eradication
Abstract
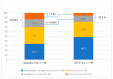
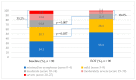
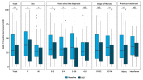
Chronic hepatitis C (CHC) is an ongoing epidemiological problem. The hepatitis C virus (HCV) may infect brain tissue, worsening mental health outcomes. The new era of highly effective oral Direct-Acting Agents (DAA) has brought a chance to eradicate the infection by 2030, however, screening campaigns are urgently needed as the majority of the infected are still undiagnosed. The aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of anxiety and depression among HCV patients, and the correlation with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in the real-world setting, before and after DAA treatment. Data on anxiety, depression, and HRQoL, were collected by using self-reported questionnaires in a single center in Poland. The study group involved 90 respondents, 50% female, with a mean age of 43.8 years. HCV eradication decreased anxiety prevalence from 30.4% to 19.1% and depression from 35.2% to 18.2%. Significant improvement in 3 out of 4 of the WHOQOL-BREF (TheWorld Health Organization Quality of Life-BREF) domains and 8 out of 10 of the HQLQv.2 domains was obtained. Anxiety diminished the somatic domain scores by 3.5 (p < 0.0001), psychological by 2.3 (p = 0.0062), social by 1.75 (p = 0.0008), and environmental by 2.68 points (p = 0.0029). Depression diminished the somatic domain scores by 3.79 (p < 0.001), psychological by 2.23 (p < 0.001), social by 1.84 (p < 0.001), and environmental by 2.42 points (p = 0.004). In the Hepatitis Quality of Life Questionnaire version 2 (HQLQ v.2), the presence of depression and/or anxiety-impaired mental health, physical health, well-being, and vitality. These results indicate the need for an active search for HCV-infective people, especially among patients in psychiatric and psychological care.
Keywords: GAD-7; HCV eradication; HQLQv.2; HRQoL; PHQ-9; WHOQOL-BREF; anxiety; depression; hepatitis C.
Conflict of interest statement
Justyna Slonka—Gilead Sciences employee, it did not affect the interpretation of the results, nor alter the authors’ adherence to MDPI policies; Damian Piotrowski—lecture fees from Abbvie; Gilead Ewa Janczewska—lecture fees, travel grants and advisory committees for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck, Roche; Arkadiusz Pisula—lecture fees, travel grants and advisory committees for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck, Roche; Joanna Musialik—lecture fees and travel grants for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck; Jerzy Jaroszewicz—lecture fees, travel grants and advisory committees for Abbvie, Gilead, Merck, Roche.
Figures

References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control . Annual Epidemiological Report for 2019. ECDC; Stockholm, Sweden: 2021. Hepatitis C.
-
- Bednarska A., Horban A., Radkowski M. Central Nervous System as a possible site of HCV replication. Przegl. Epidemiol. 2007;61:739–745. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

