Pediatric Infective Endocarditis: A Literature Review
- PMID: 35683606
- PMCID: PMC9181776
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11113217
Pediatric Infective Endocarditis: A Literature Review
Abstract
Infective endocarditis in children is a rare entity that poses multiple challenges. A history of congenital heart disease is the most common risk factor, although in recent years, other emerging predisposing conditions have gained relevance, such as central venous catheters carriers or children with chronic debilitating conditions; cases in previously healthy children with no medical history are also seen. Diagnosis is complex, although it has improved with the use of multimodal imaging techniques. Antibiotic treatment should be started early, according to causative microorganism and risk factors. Complications are frequent and continue to cause significant morbidity. Most studies have been conducted in adults and have been generalized to the pediatric population, with subsequent limitations. Our manuscript presents a comprehensive review of pediatric infective endocarditis, including recent advances in diagnosis and management.
Keywords: children; infective endocarditis; pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Unrelated to the study, Lourdes Vicent receives research funding from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain (CM20/00104).
Figures
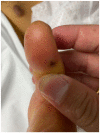
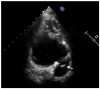
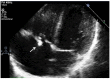
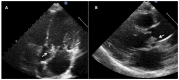
References
-
- Cresti A., Chiavarelli M., Scalese M., Nencioni C., Valentini S., Guerrini F., D’Aiello I., Picchi A., De Sensi F., Habib G. Epidemiological and Mortality Trends in Infective Endocarditis, a 17-Year Population-Based Prospective Study. Cardiovasc. Diagn. Ther. 2017;7:27–35. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2016.08.09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

