Efficacy of a Novel Intra-Articular Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma One-Week Prior to Hyaluronic Acid versus Platelet-Rich Plasma Alone in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35683635
- PMCID: PMC9181501
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11113241
Efficacy of a Novel Intra-Articular Administration of Platelet-Rich Plasma One-Week Prior to Hyaluronic Acid versus Platelet-Rich Plasma Alone in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Controlled Trial
Abstract
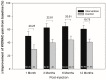
Recent studies have suggested that the combined injection of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and hyaluronic acid (HA) may have additive benefits for knee osteoarthritis over PRP alone, but there is insufficient evidence to support this combined injection. Moreover, the simultaneous injection of PRP and HA may offset the combined effect. Hence, the aim of this prospective, randomized, double-blind study was to assess their combined efficacy with a novel injection protocol. Forty-six study subjects with unilateral knee osteoarthritis were randomized to receive either a single-dose injection of HA (intervention group) or normal saline (control group) 1 week after a single-dose injection of leukocyte-poor PRP. The Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) and static balance and the risk of falls measured by Biodex Balance System were, respectively, the primary and secondary outcome measures. Evaluations were performed at baseline, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-injection. The intervention group exhibited significant declines in WOMAC pain, stiffness, and total scores, as well as static balance, compared to the control group (p < 0.05). These randomized double-blind control trials, with novel protocol of intra-articular injection of PRP 1-week prior to HA, provide greater symptom relief and improve static balance compared to PRP alone in patients with knee osteoarthritis.
Keywords: balance; hyaluronic acid; knee; osteoarthritis; platelet-rich plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad H.S., Farrag S.E., Okasha A.E., Kadry A.O., Ata T.B., Monir A.A., Shady I. Clinical outcomes are associated with changes in ultrasonographic structural appearance after platelet-rich plasma treatment for knee osteoarthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018;21:960–966. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13315. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

