Magnetite Nanoparticles in Magnetic Hyperthermia and Cancer Therapies: Challenges and Perspectives
- PMID: 35683663
- PMCID: PMC9182445
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12111807
Magnetite Nanoparticles in Magnetic Hyperthermia and Cancer Therapies: Challenges and Perspectives
Abstract
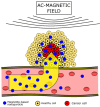
Until now, strategies used to treat cancer are imperfect, and this generates the need to search for better and safer solutions. The biggest issue is the lack of selective interaction with neoplastic cells, which is associated with occurrence of side effects and significantly reduces the effectiveness of therapies. The use of nanoparticles in cancer can counteract these problems. One of the most promising nanoparticles is magnetite. Implementation of this nanoparticle can improve various treatment methods such as hyperthermia, targeted drug delivery, cancer genotherapy, and protein therapy. In the first case, its feature makes magnetite useful in magnetic hyperthermia. Interaction of magnetite with the altered magnetic field generates heat. This process results in raised temperature only in a desired part of a patient body. In other therapies, magnetite-based nanoparticles could serve as a carrier for various types of therapeutic load. The magnetic field would direct the drug-related magnetite nanoparticles to the pathological site. Therefore, this material can be used in protein and gene therapy or drug delivery. Since the magnetite nanoparticle can be used in various types of cancer treatment, they are extensively studied. Herein, we summarize the latest finding on the applicability of the magnetite nanoparticles, also addressing the most critical problems faced by smart nanomedicine in oncological therapies.
Keywords: hyperthermia; magnetite nanoparticles; smart nanomedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

