Advances in Electrospun Hybrid Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications
- PMID: 35683685
- PMCID: PMC9181850
- DOI: 10.3390/nano12111829
Advances in Electrospun Hybrid Nanofibers for Biomedical Applications
Abstract
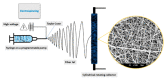
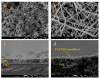
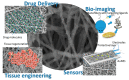
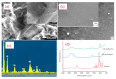
Electrospun hybrid nanofibers, based on functional agents immobilized in polymeric matrix, possess a unique combination of collective properties. These are beneficial for a wide range of applications, which include theranostics, filtration, catalysis, and tissue engineering, among others. The combination of functional agents in a nanofiber matrix offer accessibility to multifunctional nanocompartments with significantly improved mechanical, electrical, and chemical properties, along with better biocompatibility and biodegradability. This review summarizes recent work performed for the fabrication, characterization, and optimization of different hybrid nanofibers containing varieties of functional agents, such as laser ablated inorganic nanoparticles (NPs), which include, for instance, gold nanoparticles (Au NPs) and titanium nitride nanoparticles (TiNPs), perovskites, drugs, growth factors, and smart, inorganic polymers. Biocompatible and biodegradable polymers such as chitosan, cellulose, and polycaprolactone are very promising macromolecules as a nanofiber matrix for immobilizing such functional agents. The assimilation of such polymeric matrices with functional agents that possess wide varieties of characteristics require a modified approach towards electrospinning techniques such as coelectrospinning and template spinning. Additional focus within this review is devoted to the state of the art for the implementations of these approaches as viable options for the achievement of multifunctional hybrid nanofibers. Finally, recent advances and challenges, in particular, mass fabrication and prospects of hybrid nanofibers for tissue engineering and biomedical applications have been summarized.
Keywords: bone regeneration; drug delivery; electrospinning; functional agents; hybrid nanofibers; nanomedicine; nanoparticles; tissue engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
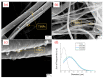
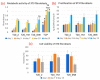
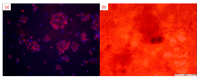
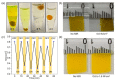
References
-
- Du L., Xu H., Zhang Y., Zou F. Electrospinning of polycaprolatone nanofibers with DMF additive: The effect of solution proprieties on jet perturbation and fiber morphologies. Fibers Polym. 2016;17:751–759. doi: 10.1007/s12221-016-6045-3. - DOI
-
- Kakoria A., Sinha-Ray S. A review on biopolymer-based fibers via electrospinning and solution blowing and their applications. Fibers. 2018;6:45. doi: 10.3390/fib6030045. - DOI
-
- Patil J.V., Mali S.S., Kamble A.S., Hong C.K., Kim J.H., Patil P.S. Electrospinning: A versatile technique for making of 1D growth of nanostructured nanofibers and its applications: An experimental approach. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017;423:641–674. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.06.116. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

