The Efficacy of Fish as an Early Complementary Food on the Linear Growth of Infants Aged 6-7 Months: A Randomised Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35683991
- PMCID: PMC9182483
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14112191
The Efficacy of Fish as an Early Complementary Food on the Linear Growth of Infants Aged 6-7 Months: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
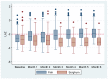
Fish is a good animal-source protein for growth and development. The main objective of the study was to assess the efficacy of fish during the early complementary feeding period on infants' linear growth in the Samfya district of the Luapula Province of Zambia in 6 months randomised controlled trial. The study was conducted from April 2019 to January 2020. Infants aged 6-7 months (N = 238) were assigned to either the intervention (treatment) group or control (placebo) group to receive fish powder or sorghum powder, respectively. Participants were followed on a weekly basis to distribute the powder and record compliance/usage and any morbidities. Anthropometric measurements were taken monthly. A linear mixed-effects model showed that fish powder improved linear growth among infants over all the 6 months of the intervention period. The fish powder increased length-for-age z scores by 1.26 (95% CI: 0.94-1.57) and weight-for-age z score by 0.95 (95% CI 0.6-1.23). The addition of fish powder to the infant's usual food during the early complementary feeding improves the infant's linear growth outcome.
Keywords: Zambia; complementary feeding; fish; growth; infants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yohannes T., Laelago T., Ayele M., Tamrat T. Mortality and morbidity trends and predictors of mortality in under-five children with severe acute malnutrition in Hadiya zone, South Ethiopia: A four-year retrospective review of hospital-based records (2012–2015) BMC Nutr. 2017;3:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s40795-017-0135-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Group Levels and Trends in Child Malnutrition. Key Findings of the 2018 Edition. 2018. [(accessed on 2 February 2018)]. pp. 1–16. Available online: http://www.who.int/nutgrowthdb/jme_brochoure2017.pdf?ua=1.
-
- de Onis M., Martines J., Onyango A., Pinol A., World Health Organization. Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group . WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development. WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2006. p. 339.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous