The Neuroprotective Effects of Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma Supplementation Involve the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis
- PMID: 35684013
- PMCID: PMC9183112
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14112211
The Neuroprotective Effects of Spray-Dried Porcine Plasma Supplementation Involve the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis
Abstract
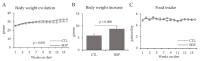
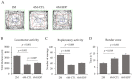
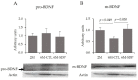
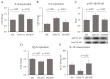
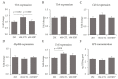
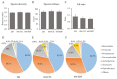
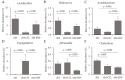
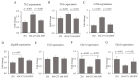
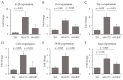
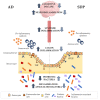
Dietary supplementation with spray-dried porcine plasma (SDP) reduces the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) hallmarks in SAMP8 mice. Since gut microbiota can play a critical role in the AD progression, we have studied if the neuroprotective effects of SDP involve the microbiota−gut−brain axis. Experiments were performed on two-month-old SAMP8 mice fed a standard diet and on six-month-old SAMP8 mice fed a control diet or an 8% SDP supplemented diet for four months. Senescence impaired short- and long-term memory, reduced cortical brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) abundance, increased interleukin (Il)-1β, Il-6, and Toll-like receptor 2 (Tlr2) expression, and reduced transforming growth factor β (Tgf-β) expression and IL-10 concentration (all p < 0.05) and these effects were mitigated by SDP (all p < 0.05). Aging also increased pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum and colon (all p < 0.05). SDP attenuated both colonic and systemic inflammation in aged mice (all p < 0.05). SDP induced the proliferation of health-promoting bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Pediococcus, while reducing the abundance of inflammation-associated bacteria, such as Johnsonella and Erysipelothrix (both q < 0.1). In conclusion, SDP has mucosal and systemic anti-inflammatory effects as well as neuroprotective properties in senescent mice; these effects are well correlated with SDP promotion of the abundance of probiotic species, which indicates that the gut−brain axis could be involved in the peripheral effects of SDP supplementation.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; aging; dietary supplementation; microbiota; spray-dried porcine plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
C.R.-C., C.A., C.G.-F., M.P., A.P.-B., M.M. and L.M. have no conflict of interests. J.P. is employed by APC-Europe S.L.U. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
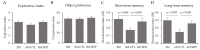

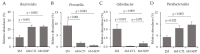
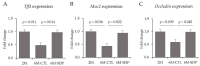
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

