Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation Alone and Combined with Resistance Exercise on Skeletal Muscle in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35684018
- PMCID: PMC9182791
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14112221
Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation Alone and Combined with Resistance Exercise on Skeletal Muscle in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
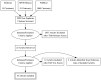
Sarcopenia negatively affects skeletal muscle mass and function in older adults. Omega-3 (ω-3) fatty acid supplementation, with or without resistance exercise training (RET), is suggested to play a role as a therapeutic component to prevent or treat the negative effects of sarcopenia. A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted on the impact of ω-3 fatty acid supplementation with or without RET on measures of muscle mass and function in older adults (≥55 y). The data sources included SPORTDiscus, PubMed, and Medline. All the study types involving ω-3 fatty acid supplementation on measures of muscle mass and function in older adults (without disease) were included. The mean differences (MDs) or standardized mean differences (SMDs) with 95% confidence intervals were calculated and pooled effects assessed. Sixteen studies (1660 females, 778 males) met our inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis. ω-3 fatty acid supplementation did not impact lean tissue mass (SMD 0.09 [-0.10, 0.28]). Benefits were observed for lower body strength (SMD 0.54 [0.33, 0.75]), timed-up-and-go (MD 0.29 [0.23, 0.35]s), and 30-s sit-to-stand performance (MD 1.93 [1.59, 2.26] repetitions) but not walking performance (SMD -0.01 [-0.10, 0.07]) or upper body strength (SMD 0.05 [-0.04, 0.13]). Supplementing with ω-3 fatty acids may improve the lower-body strength and functionality in older adults.
Keywords: PUFA; anabolism; elderly; inflammation; sarcopenia; strength.
Conflict of interest statement
D.M.C. is affiliated with the Pan Am Clinic Foundation which receives general education and research support from ConMed Linvatec, Ossur, Zimmer Biomet, and Arthrex.
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

