Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents
- PMID: 35684098
- PMCID: PMC9182680
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14112296
Vitamin D Supplementation on Carotid Remodeling and Stiffness in Obese Adolescents
Abstract
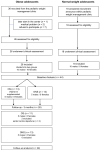
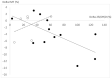
Obesity is associated with vitamin D (VD) deficiency and arterial stiffness. This randomized control trial assessed the effects of VD supplementation during a weight-loss program on carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and carotid compliance in obese adolescents. Participants were randomly assigned to receive either a 12-week lifestyle program with VD supplementation (n = 13), a lifestyle program without VD supplementation (n = 13) or a control group composed of normal-weight adolescents (n = 18). Serum total and free 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D), IMT and carotid compliance were measured before and after the trial. Insufficiency in 25(OH)D concentration was found in 73% of obese participants compared to 22% among controls. Obese adolescents had lower free 25(OH)D and displayed higher IMT but lower carotid compliance than controls. Free 25(OH)D and IMT were negatively correlated in adolescents displaying VD insufficiency at baseline. After three months, total and free 25(OH)D increased in both groups. The changes of IMT and carotid compliance were similar between groups. The changes in IMT were correlated with the changes in total 25(OH)D in obese adolescents with VD insufficiency at baseline (r = -0.59, p = 0.03). While the lifestyle program with VD supplementation did not affect carotid compliance, IMT reduction was improved in obese adolescents.
Keywords: arterial stiffness; childhood obesity; intima-media thickness; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ganji V., Zhang X., Shaikh N., Tangpricha V. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with prevalence of metabolic syndrome and various cardiometabolic risk factors in US children and adolescents based on assay-adjusted serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data from NHANES 2001–2006. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011;94:225–233. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.013516. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Al Mheid I., Patel R., Murrow J., Morris A., Rahman A., Fike L., Kavtaradze N., Uphoff I., Hooper C., Tangpricha V., et al. Vitamin D status is associated with arterial stiffness and vascular dysfunction in healthy humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011;8:186–192. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.051. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

