The Integrative Effects of Biochar and ZnO Nanoparticles for Enhancing Rice Productivity and Water Use Efficiency under Irrigation Deficit Conditions
- PMID: 35684189
- PMCID: PMC9183004
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11111416
The Integrative Effects of Biochar and ZnO Nanoparticles for Enhancing Rice Productivity and Water Use Efficiency under Irrigation Deficit Conditions
Abstract
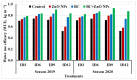
Water stress is considered one of the most environmental hazards that threaten agricultural productivity. Therefore, two field experiments were conducted to investigate the impact of biochar (6 t ha-1 as soil amendment), ZnO NPs (50 mg L-1 as foliar application), and their combination on growth, yield, and water use efficiency (WUE) of rice grown under four irrigation deficit treatments (i.e., irrigation every 3, 6, 9 and 12 d). The irrigation every 3 d was considered as the control in the current study. For this purpose, biochar was prepared through the pyrolysis of corn stalk and rice husk at 350 °C for 3 h, while sonochemical combined with the precipitation method was used to prepare zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) from zinc acetate. The morphological structures of the produced biochar and ZnO NPs were characterized using X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 gas adsorption-desorption, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The results exhibited that the combination of biochar alongside ZnO NPs resulted in a positive significant effect on the physiological traits such as chlorophyll content, relative water content, plant height, and leaf area index as well as yield-associated components (i.e., number of panicles m-2, number of filled grain per panicle, 1000-grain weight), and biological and grain yield ha-1 when rice plants were irrigated every 9 days without a significant difference with those obtained from the control treatment (irrigation every 3 d). In conclusion, the combination of biochar and ZnO NPs could be recommended as an optimal approach to maximize both grain yield ha-1 and WUE of rice.
Keywords: biochar; deficit irrigation; productivity; rice; water use efficiency; zinc oxide NPs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Seleiman M.F., Elshayb O.M., Nada A.M., El-leithy S.A., Baz L., Alhammad B.A., Mahdi A.H.A. Azolla Compost as an Approach for Enhancing Growth, Productivity and Nutrient Uptake of Oryza sativa L. Agronomy. 2022;12:416. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12020416. - DOI
-
- Prasad R., Shivay Y.S., Kumar D. Rice Production Worldwide. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2017. Current status, challenges, and opportunities in rice production; pp. 1–32.
-
- Abu-hashim M., Negm A. Sustainability of Agricultural Environment in Egypt: Part I. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2018. Deficit irrigation management as strategy under conditions of water scarcity; potential application in North Sinai, Egypt; pp. 35–55.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

