Insights into Aptamer-Drug Delivery Systems against Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 35684384
- PMCID: PMC9182114
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27113446
Insights into Aptamer-Drug Delivery Systems against Prostate Cancer
Abstract
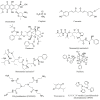
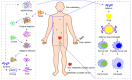
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in elderly males. Significant progress has been made in the drug therapies for prostate cancer in recent years. However, side effects are still problems that have not been overcome by the currently used anti-prostate cancer drugs. Novel technologies can be applied to reduce or even eliminate the side effects of drugs. An aptamer may be a sequence of nucleic acids or peptides that can specifically recognize proteins or cells. Taking advantage of this feature, scientists have designed aptamer-drug delivery systems for the development of anti-prostate cancer agents. Theoretically, these aptamer-drug delivery systems can specifically recognize prostate cancer cells and then induce cell death without attacking normal cells. We collected the relevant literature in this field and found that at least nine compounds have been prepared as aptamer-drug delivery systems to evaluate their precise anti-prostate cancer effects. However, the currently studied aptamer-drug delivery systems have not yet entered the market due to defects. Here, we analyze the published data, summarize the characteristics of these delivery systems, and propose ways to promote their application, thus promoting the development of the aptamer-drug delivery systems against prostate cancer.
Keywords: aptamer; curcumin; docetaxel; doxorubicin; drug delivery systems; paclitaxel; prostate cancer; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A RNA-DNA Hybrid Aptamer for Nanoparticle-Based Prostate Tumor Targeted Drug Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Mar 14;17(3):380. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030380. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26985893 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-aptamer-based delivery vehicle of doxorubicin to both PSMA (+) and PSMA (-) prostate cancers.Biomaterials. 2011 Mar;32(8):2124-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.11.035. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21147500
-
Smart ligand: aptamer-mediated targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs and siRNA for cancer therapy.J Control Release. 2013 Oct 28;171(2):152-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.06.006. Epub 2013 Jun 15. J Control Release. 2013. PMID: 23777885 Review.
-
RNA aptamer-conjugated liposome as an efficient anticancer drug delivery vehicle targeting cancer cells in vivo.J Control Release. 2014 Dec 28;196:234-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.10.018. Epub 2014 Oct 24. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 25450401
-
Aptamer-Mediated Polymeric Vehicles for Enhanced Cell-Targeted Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Targets. 2018 Feb 8;19(3):248-258. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666160617120926. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 27321771 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of aptamer functionalized nanomaterials in targeting therapeutics of typical tumors.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 16;11:1092901. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1092901. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36873354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New insights and options into the mechanisms and effects of combined targeted therapy and immunotherapy in prostate cancer.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Apr 29;29:91-106. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.04.007. eCollection 2023 Jun 15. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 37215386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell and bulk RNA-sequencing analysis to predict the role and clinical value of CD36 in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 10;9(11):e22201. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22201. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034730 Free PMC article.
-
Natural anti-cancer products: insights from herbal medicine.Chin Med. 2025 Jun 9;20(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01124-y. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40490812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of CKAP2 as a Potential Target for Prevention of Gastric Cancer Progression: A Multi-Omics Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 12;26(4):1557. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041557. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004022 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AD20159033/Specific Research Project of Guangxi for Research Bases and Talents
- 2018GXNSFBA281043/Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi
- 2021003/development program of high-level talent team under Qihuang project of Guangxi university of Chinese medicine
- 05019055/Special Fund for Bagui Scholars of Guangxi
- 81902764/National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

