Lipids in Archaeological Pottery: A Review on Their Sampling and Extraction Techniques
- PMID: 35684389
- PMCID: PMC9182108
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27113451
Lipids in Archaeological Pottery: A Review on Their Sampling and Extraction Techniques
Abstract
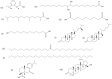
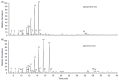
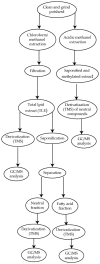
Several studies have been performed so far for the effective recovery, detection and quantification of specific compounds and their degradation products in archaeological materials. According to the literature, lipid molecules are the most durable and widespread biomarkers in ancient pottery. Artificial ageing studies to simulate lipid alterations over time have been reported. In this review, specific lipid archaeological biomarkers and well-established sampling and extraction methodologies are discussed. Although suitable analytical techniques have unraveled archaeological questions, some issues remain open such as the need to introduce innovative and miniaturized protocols to avoid extractions with organic solvents, which are often laborious and non-environmentally friendly.
Keywords: ageing study; ancient pottery; archaeological biomarkers; lipid derivatization; lipid extraction; lipids in pottery; sampling of lipids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dunne J., Chapman A., Blinkhorn P., Evershed R.P. Fit for purpose? Organic residue analysis and vessel specialisation: The perfectly utilitarian medieval pottery assemblage from West Cotton, Raunds. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2020;120:105178. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2020.105178. - DOI
-
- Lundy J., Drieu L., Meo A., Sacco V., Arcifa L., Pezzini E., Aniceti V., Fiorentino G., Alexander M., Orecchioni P., et al. New insights into early medieval Islamic cuisine: Organic residue analysis of pottery from rural and urban Sicily. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0252225. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252225. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tanasi D., Greco E., Noor R.E., Feola S., Kumar V., Crispino A., Gelis I. 1H NMR, 1H–1H 2D TOCSY and GC-MS analyses for the identification of olive oil in Early Bronze Age pottery from Castelluccio (Noto, Italy) Anal. Methods. 2018;10:2756–2763. doi: 10.1039/C8AY00420J. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

