Lignin as a Natural Carrier for the Efficient Delivery of Bioactive Compounds: From Waste to Health
- PMID: 35684534
- PMCID: PMC9182000
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27113598
Lignin as a Natural Carrier for the Efficient Delivery of Bioactive Compounds: From Waste to Health
Abstract
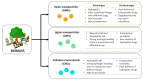
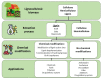
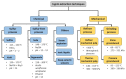
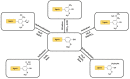
Lignin is a fascinating aromatic biopolymer with high valorization potentiality. Besides its extensive value in the biorefinery context, as a renewable source of aromatics lignin is currently under evaluation for its huge potential in biomedical applications. Besides the specific antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of lignin, that depend on its source and isolation procedure, remarkable progress has been made, over the last five years, in the isolation, functionalization and modification of lignin and lignin-derived compounds to use as carriers for biologically active substances. The aim of this review is to summarize the current state of the art in the field of lignin-based carrier systems, highlighting the most important results. Furthermore, the possibilities and constraints related to the physico-chemical properties of the lignin source will be reviewed herein as well as the modifications and processing required to make lignin suitable for the loading and release of active compounds.
Keywords: drug carrier; extraction techniques; lignin; nanoparticles; renewable material.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Wang F., Ouyang D., Zhou Z., Page S.J., Liu D., Zhao X. Lignocellulosic biomass as sustainable feedstock and materials for power generation and energy storage. J. Energy Chem. 2021;57:247–280. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2020.08.060. - DOI
-
- Calcio Gaudino E., Cravotto G., Manzoli M., Tabasso S. From waste biomass to chemicals and energy: Via microwave-assisted processes. Green Chem. 2019;21:1202–1235. doi: 10.1039/C8GC03908A. - DOI
-
- Valentine J., Clifton-Brown J., Hastings A., Robson P., Allison G., Smith P. Food vs. fuel: The use of land for lignocellulosic ‘next generation’ energy crops that minimize competition with primary food production. GCB Bioenergy. 2011;4:1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1757-1707.2011.01111.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

