Automatic Cognitive Fatigue Detection Using Wearable fNIRS and Machine Learning
- PMID: 35684626
- PMCID: PMC9183003
- DOI: 10.3390/s22114010
Automatic Cognitive Fatigue Detection Using Wearable fNIRS and Machine Learning
Abstract
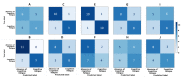
Wearable sensors have increasingly been applied in healthcare to generate data and monitor patients unobtrusively. Their application for Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI) allows for unobtrusively monitoring one's cognitive state over time. A particular state relevant in multiple domains is cognitive fatigue, which may impact performance and attention, among other capabilities. The monitoring of this state will be applied in real learning settings to detect and advise on effective break periods. In this study, two functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) wearable devices were employed to build a BCI to automatically detect the state of cognitive fatigue using machine learning algorithms. An experimental procedure was developed to effectively induce cognitive fatigue that included a close-to-real digital lesson and two standard cognitive tasks: Corsi-Block task and a concentration task. Machine learning models were user-tuned to account for the individual dynamics of each participant, reaching classification accuracy scores of around 70.91 ± 13.67 %. We concluded that, although effective for some subjects, the methodology needs to be individually validated before being applied. Moreover, time on task was not a particularly determining factor for classification, i.e., to induce cognitive fatigue. Further research will include other physiological signals and human-computer interaction variables.
Keywords: brain–computer interface; cognitive fatigue; functional near-infrared spectroscopy; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
R.V., H.S. and H.G. are affiliated with PLUX Wireless Biosignals, the company that produces the acquisition devices used in this work and also the software used to acquire the physiological signals.
Figures



References
-
- Henriksen A., Haugen Mikalsen M., Woldaregay A.Z., Muzny M., Hartvigsen G., Hopstock L.A., Grimsgaard S. Using Fitness Trackers and Smartwatches to Measure Physical Activity in Research: Analysis of Consumer Wrist-Worn Wearables. J. Med. Internet. Res. 2018;20:e110. doi: 10.2196/jmir.9157. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Udovičić G., Topić A., Russo M. Wearable technologies for smart environments: A review with emphasis on BCI; Proceedings of the 2016 24th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks, SoftCOM 2016; Split, Croatia. 22–24 September 2016; - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

