Mechanistic insights into the chemistry of compound I formation in heme peroxidases: quantum chemical investigations of cytochrome c peroxidase
- PMID: 35685178
- PMCID: PMC9125774
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra01073a
Mechanistic insights into the chemistry of compound I formation in heme peroxidases: quantum chemical investigations of cytochrome c peroxidase
Abstract
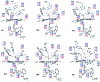
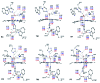
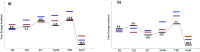
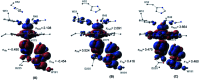
Peroxidases are heme containing enzymes that catalyze peroxide-dependant oxidation of a variety of substrates through forming key ferryl intermediates, compounds I and II. Cytochrome c peroxidase (Ccp1) has served for decades as a chemical model toward understanding the chemical biology of this heme family of enzymes. It is known to feature a distinctive electronic behaviour for its compound I despite significant structural similarity to other peroxidases. A water-assisted mechanism has been proposed over a dry one for the formation of compound I in similar peroxidases. To better identify the viability of these mechanisms, we employed quantum chemistry calculations for the heme pocket of Ccp1 in three different spin states. We provided comparative energetic and structural results for the six possible pathways that suggest the preference of the dry mechanism energetically and structurally. The doublet state is found to be the most preferable spin state for the mechanism to proceed and for the formation of the Cpd I ferryl-intermediate irrespective of the considered dielectric constant used to represent the solvent environment. The nature of the spin state has negligible effects on the calculated structures but great impact on the energetics. Our analysis was also expanded to explain the major contribution of key residues to the peroxidase activity of Ccp1 through exploring the mechanism at various in silico generated Ccp1 variants. Overall, we provide valuable findings toward solving the current ambiguity of the exact mechanism in Ccp1, which could be applied to peroxidases with similar heme pockets.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
I declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Reedy C. J. Gibney B. R. Heme Protein Assemblies. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:617–650. - PubMed
-
- Smulevich G. Feis A. Howes B. D. Fifteen Years of Raman Spectroscopy of Engineered Heme Containing Peroxidases: What Have We Learned? Acc. Chem. Res. 2005;38:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Moody P. C. E. Raven E. L. The Nature and Reactivity of Ferryl Heme in Compounds I and II. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018;51:427–435. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

