Chronic and Binge Alcohol Ingestion Increases Truncated Oxidized Phosphatidylcholines in Mice Lungs Due to Increased Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 35685280
- PMCID: PMC9171009
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2022.860449
Chronic and Binge Alcohol Ingestion Increases Truncated Oxidized Phosphatidylcholines in Mice Lungs Due to Increased Oxidative Stress
Abstract
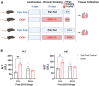
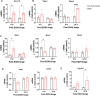
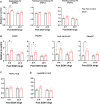
Heavy alcohol drinking has negative health effects in multiple organs. It predisposes lungs to inflammatory conditions associated with acute lung injury and increased incidence of pneumonia and sepsis, which may lead to death due to acute respiratory distress syndrome in some individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD). In general, rodent models of alcohol exposure either do not recapitulate multiple organ injuries as seen in humans or require longer duration to establish tissue injury and inflammation. The recently introduced NIAAA model of alcohol-induced liver injury, characterized by a marked increase in steatosis and liver damage with 10 days of a liquid diet containing 5% ethanol followed by a single ethanol binge (5 g/kg). Therefore, we employed this model to explore the status of surfactant phospholipids, oxidative stress, tissue injury markers and inflammatory cytokines in lungs. In lungs of C57BL/6J mice, the alcohol feeding significantly increased levels of the surfactant phospholipid dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine (DPPC) as well as the truncated oxidized phosphatidylcholines palmitoyl oxovaleryl phosphatidyl-choline (POVPC), palmitoyl glutaryl phosphatidyl-choline (PGPC), palmitoyl oxo-nonanoyl phosphatidyl-choline (ALDO-PC), and palmitoyl azelaoyl phosphatidyl-choline (PAzePC) at 9 h post-binge. Additionally, gene expression of the enzymes catalyzing lipid oxidation, such as arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase (Alox15), prostaglandin synthase 2 (Ptgs2), Cytochrome P450 2E1 (Cyp2E1) and NADPH oxidase 1 (Nox1) were significantly increased. Furthermore, ethanol increased levels of the inflammatory cytokine Interleukin-17 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. In conclusion, the NIAAA alcohol feeding model might be suitable to study alcohol-induced lung injury and inflammation.
Keywords: IL-17; LPS; PGPC; POVPC; alcohol; lung injury; oxidized phospholipids.
Copyright © 2022 Appolonia, Wolf, Zawatsky and Cinar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elevated truncated oxidized phospholipids as a factor exacerbating ALI in the aging lungs.FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3887-3900. doi: 10.1096/fj.201800981R. Epub 2018 Dec 6. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30521374 Free PMC article.
-
Surfactant phospholipids, surfactant proteins, and inflammatory markers during acute lung injury in children.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2010 Jan;11(1):82-91. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3181ae5a4c. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2010. PMID: 19550365
-
Chronic + binge alcohol exposure promotes inflammation and alters airway mechanics in the lung.Alcohol. 2019 Nov;80:53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Alcohol. 2019. PMID: 30445135 Free PMC article.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Alcoholic lung injury: metabolic, biochemical and immunological aspects.Toxicol Lett. 2013 Oct 24;222(2):171-9. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.07.016. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Toxicol Lett. 2013. PMID: 23892124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alcohol and e-cigarette damage alveolar-epithelial barrier by activation of P2X7r and provoke brain endothelial injury via extracellular vesicles.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 15;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01461-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38225580 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol and e-cigarette damage alveolar-epithelial barrier by activation of P2X7r and provoke brain endothelial injury via extracellular vesicles.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 14:rs.3.rs-3552555. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3552555/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 15;22(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01461-1. PMID: 38014253 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Association between oxidative balance score and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A cross-sectional study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Oct 4;103(40):e39883. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039883. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39465700 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative balance score and its association with chronic inflammatory airway diseases and mortality: a population-based study.Front Nutr. 2025 Jan 22;12:1541559. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1541559. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39911804 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Therapeutic Potential of Sulfonyl Urea Derivatives as Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (sEH) Inhibitors.Molecules. 2024 Jun 26;29(13):3036. doi: 10.3390/molecules29133036. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38998987 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

