Nondirected Living Kidney Donation and Recipient Outcomes in the United States: A 20-Year Review
- PMID: 35685320
- PMCID: PMC9171626
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.03.012
Nondirected Living Kidney Donation and Recipient Outcomes in the United States: A 20-Year Review
Abstract
Introduction: Nondirected donation (NDD) of the kidneys is a growing practice where donors who do not have any genetic or emotional relationship are selected to donate to a wide variety of recipients with a range of selection criteria and decisions which are left up to individual transplant centers.
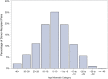
Methods: We review all adult living kidney donor-recipient (DR) pairs and outcomes from NDDs who were recorded in United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) database as code 10 (anonymous) from October 1997 to September 2017 for demographics and outcomes.
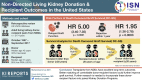
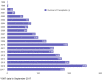
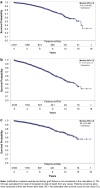
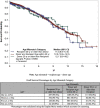
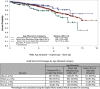
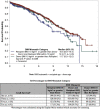
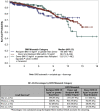
Results: A total of 2174 DR pairs were identified. The number of NDDs increased from 18 in 2000 to 256 in 2016. Survival analysis showed higher death-censored-graft survival (DC-GS) when recipient was 20 years or more older than donor followed by recipient-donor within 20 years of age and lowest when donor was 20 years or more older than recipient (P = 0.0114).
Conclusion: Overall, the number of NDDs has increased significantly in the 20-year review period. Transplants from NDDs have excellent long-term outcomes. Better matching of controllable DR factors, such as age and body mass index (BMI), could further improve GS. Further research is needed to incorporate these DR factors into paired kidney donation programs potentially enhancing the utility and beneficence of this invaluable donation.
Keywords: donor-recipient matching; living kidney donation; nondirected kidney donation; paired exchange.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier, Inc., on behalf of the International Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- United States Renal Data System USRDS Previous ADRs. United States Renal Data System USRDS. Published 2019. https://usrds.org/annual-data-report/previous-adrs/
-
- OPTN 2018 Annual report of the U.S. Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network and the Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients. OPTN. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/annual-report/ Published 2018.
-
- National Institutes of Health, US Renal Data System 2019 USRDS Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, US Renal Data System. https://usrds.org/media/2371/2019-executive-summary.pdf Published 2019.
-
- HRSA Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network: National Data. HRSA. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/data/view-data-reports/national-data/ Published 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

