A Novel Risk-Prediction Scoring System for Sepsis among Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of a Large Clinical Database
- PMID: 35685488
- PMCID: PMC9159144
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5435656
A Novel Risk-Prediction Scoring System for Sepsis among Patients with Acute Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Analysis of a Large Clinical Database
Abstract
Background: The prognosis is poor when acute pancreatitis (AP) progresses to sepsis; therefore, it is necessary to accurately predict the probability of sepsis and develop a personalized treatment plan to reduce the disease burden of AP patients.
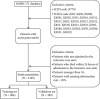
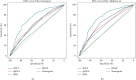
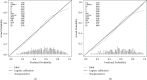
Methods: A total of 1295 patients with AP and 43 variables were extracted from the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC) IV database. The included patients were randomly assigned to the training set and to the validation set at a ratio of 7 : 3. The chi-square test or Fisher's exact test was used to test the distribution of categorical variables, and Student's t-test was used for continuous variables. Multivariate logistic regression was used to establish a prognostic model for predicting the occurrence of sepsis in AP patients. The indicators to verify the overall performance of the model included the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curves, the net reclassification improvement (NRI), the integrated discrimination improvement (IDI), and a decision curve analysis (DCA).
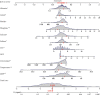
Results: The multifactor analysis results showed that temperature, phosphate, calcium, lactate, the mean blood pressure (MBP), urinary output, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI), sodium, platelet count, and albumin were independent risk factors. All of the indicators proved that the prediction performance and clinical profitability of the newly established nomogram were better than those of other common indicators (including SIRS, BISAP, SOFA, and qSOFA).
Conclusions: The new risk-prediction system that was established in this research can accurately predict the probability of sepsis in patients with acute pancreatitis, and this helps clinicians formulate personalized treatment plans for patients. The new model can reduce the disease burden of patients and can contribute to the reasonable allocation of medical resources, which is significant for tertiary prevention.
Copyright © 2022 Aozi Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest and consent for publication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Construction and validation of machine learning models for sepsis prediction in patients with acute pancreatitis.BMC Surg. 2023 Sep 1;23(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12893-023-02151-y. BMC Surg. 2023. PMID: 37658375 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Construction and validation of a risk assessment model for acute kidney injury in patients with acute pancreatitis in the intensive care unit.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Oct 26;24(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03369-x. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37884898 Free PMC article.
-
Improved prediction of sepsis-associated encephalopathy in intensive care unit sepsis patients with an innovative nomogram tool.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 20;15:1344004. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1344004. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38445262 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Novel Nomogram Incorporating Red Blood Cell Distribution Width-Albumin Ratio for the Prediction of 30-day Mortality in Acute Pancreatitis Patients.Emerg Med Int. 2022 Nov 28;2022:1573931. doi: 10.1155/2022/1573931. eCollection 2022. Emerg Med Int. 2022. PMID: 36478954 Free PMC article.
-
Nomogram predictive model for in-hospital mortality risk in elderly ICU patients with urosepsis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Apr 26;24(1):442. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09319-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38671376 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association between serum creatinine to albumin ratio and short- and long-term all-cause mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis admitted to the intensive care unit: a retrospective analysis based on the MIMIC-IV database.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 15;15:1373371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1373371. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38686375 Free PMC article.
-
Amphipathic Liponecrosis Impairs Bacterial Clearance and Causes Infection During Sterile Inflammation.Gastroenterology. 2023 Oct;165(4):999-1015. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.05.034. Epub 2023 May 30. Gastroenterology. 2023. PMID: 37263302 Free PMC article.
-
Machine Learning Predictive Model for Septic Shock in Acute Pancreatitis with Sepsis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Mar 5;17:1443-1452. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S441591. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38481478 Free PMC article.
-
Acute pancreatitis: A review of diagnosis, severity prediction and prognosis assessment from imaging technology, scoring system and artificial intelligence.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Oct 7;29(37):5268-5291. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i37.5268. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37899784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing a predictive model for septic shock risk in acute pancreatitis patients using interpretable machine learning algorithms.Digit Health. 2025 May 25;11:20552076251346361. doi: 10.1177/20552076251346361. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2025. PMID: 40433305 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
