Transcatheter Angiographic Embolization of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy-Related Bleeding: A Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 35685502
- PMCID: PMC9158794
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4422547
Transcatheter Angiographic Embolization of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy-Related Bleeding: A Single-Center Experience
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the clinical characteristics and angiographic features of transcatheter angiographic embolization (TAE) in patients with active bleeding after percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL).
Methods: Between 2009 and 2018, 45 patients who underwent TAE for hemorrhage control after PCNL were reviewed retrospectively. Patient clinical characteristics and angiographic features of TAE were analyzed.
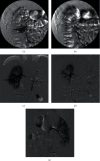
Results: Of the 3148 patients, 45 (1.4%) patients were treated with TAE after PCNL. The interval from the bleeding episode to TAE was 3 days (1,6). Arterial laceration, arteriovenous fistula, and negative angiographic finding were found in 28 (62.2%), 7 (15.6%), and 10 patients (22.2%). Thirty-five patients (92.1%) achieved primary clinical success. The median-corrected hemoglobin decrease from bleeding episode to TAE was 52 g/L (25.25, 71.00). The median-corrected hemoglobin decrease rate from bleeding episode to TAE was 13.11 g/L·d (5.60, 26.12). The hemoglobin decrease from bleeding episode to TAE was lesser in negative angiographic patients (28.50 (10.75,51.25) g/L VS 53.7 (35.0,73.13) g/L) than in positive angiographic patients (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: TAE is a safe and effective treatment for post-PCNL bleeding patients. Previous kidney surgery is associated with a higher risk of TAE. Patients with bleeding from multiple negative angiographic findings can be considered for prophylactic embolization.
Copyright © 2022 Fan Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Skolarikos A., Neisius A., Petřík A., Somani B., Thomas K., Gambaro G. Guideline on Urolithiasis . Arnhem, Netherlands: European association of urology; 2018.
-
- Thomas K., Francisco D., Janak D., et al. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: technique. World Journal of Urology . 2017;35(9):1361–1368. - PubMed
-
- Zeng G., Zhao Z., Wan S., et al. Failure of initial renal arterial embolization for severe post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy hemorrhage: multi-center study of risk factors. Journal of Urology . 2013;190:2133–2138. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
