Antibiotic resistance: bioinformatics-based understanding as a functional strategy for drug design
- PMID: 35685616
- PMCID: PMC9122625
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra01484b
Antibiotic resistance: bioinformatics-based understanding as a functional strategy for drug design
Abstract
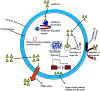
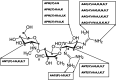
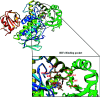
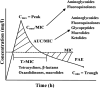
The use of antibiotics to manage infectious diseases dates back to ancient civilization, but the lack of a clear distinction between the therapeutic and toxic dose has been a major challenge. This precipitates the notion that antibiotic resistance was from time immemorial, principally because of a lack of adequate knowledge of therapeutic doses and continuous exposure of these bacteria to suboptimal plasma concentration of antibiotics. With the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming in 1924, a milestone in bacterial infections' treatment was achieved. This forms the foundation for the modern era of antibiotic drugs. Antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, quinolones, tetracycline, macrolides, sulphonamides, aminoglycosides and glycopeptides are the mainstay in managing severe bacterial infections, but resistant strains of bacteria have emerged and hampered the progress of research in this field. Recently, new approaches to research involving bacteria resistance to antibiotics have appeared; these involve combining the molecular understanding of bacteria systems with the knowledge of bioinformatics. Consequently, many molecules have been developed to curb resistance associated with different bacterial infections. However, because of increased emphasis on the clinical relevance of antibiotics, the synergy between in silico study and in vivo study is well cemented and this facilitates the discovery of potent antibiotics. In this review, we seek to give an overview of earlier reviews and molecular and structural understanding of bacteria resistance to antibiotics, while focusing on the recent bioinformatics approach to antibacterial drug discovery.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no financial and intellectual conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Surveillance of antibiotic resistance and antibiotic consumption in Medimurje].Acta Med Croatica. 2004;58(4):285-91. Acta Med Croatica. 2004. PMID: 15700684 Croatian.
-
[The history of the development and changes of quinolone antibacterial agents].Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003;38(2):161-79. Yakushigaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 15143768 Japanese.
-
[Antibiotic susceptibility analysis of Enterococcus spp. isolated from urine].Przegl Lek. 2004;61(5):473-6. Przegl Lek. 2004. PMID: 15515808 Polish.
-
Antibiotic Discovery: Where Have We Come from, Where Do We Go?Antibiotics (Basel). 2019 Apr 24;8(2):45. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics8020045. Antibiotics (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31022923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targets for design of novel inhibitors to circumvent aminoglycoside resistance.Curr Drug Targets. 2005 May;6(3):353-61. doi: 10.2174/1389450053765860. Curr Drug Targets. 2005. PMID: 15857293 Review.
Cited by
-
Sterically Hindered Quaternary Phosphonium Salts (QPSs): Antimicrobial Activity and Hemolytic and Cytotoxic Properties.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 22;23(1):86. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010086. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008507 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Gram-negative bacteria for novel anti-Gram-negative antibiotics.Microb Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;17(11):e70032. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70032. Microb Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39487848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origin of Antibiotics and Antibiotic Resistance, and Their Impacts on Drug Development: A Narrative Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Nov 15;16(11):1615. doi: 10.3390/ph16111615. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella enterica Serovar Gallinarum Biovars Pullorum and Gallinarum in Poultry: Review of Pathogenesis, Antibiotic Resistance, Diagnosis and Control in the Genomic Era.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Dec 25;13(1):23. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13010023. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38247582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibiotic Discovery and Resistance: The Chase and the Race.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 30;11(2):182. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11020182. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35203785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wainwright M. Moulds in ancient and more recent medicine. Mycologist. 1989;3:21–23. doi: 10.1016/S0269-915X(89)80010-2. - DOI
-
- Biggest Threats and Data|Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance, CDC
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

