Evolutionary Game Analysis of Construction Workers' Unsafe Behaviors Based on Incentive and Punishment Mechanisms
- PMID: 35686084
- PMCID: PMC9172908
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.907382
Evolutionary Game Analysis of Construction Workers' Unsafe Behaviors Based on Incentive and Punishment Mechanisms
Abstract
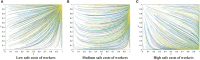
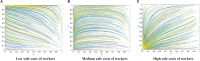
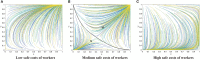
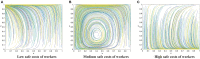
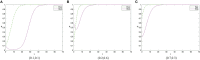
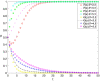
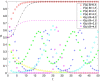
Construction is one of the most dangerous industries because of its open working environment and risky construction conditions. In the process of construction, risk events cause great losses for owners and workers. Most of the risk events are closely related to unsafe behaviors of workers. Therefore, it is of great significance for contractors to establish management measures, e.g., incentive and punishment mechanism, to induce workers to reduce unsafe behaviors. This paper aims to take the incentive and punishment mechanism into consideration and develop an evolutionary game model to improve the effectiveness of safety management. The evolutionary stability strategies which can help reduce unsafe behaviors are obtained and analyzed. Results show that there are 12 equilibrium strategies under the condition of different parameters. Specifically, the incentive and punishment mechanism has played an important role for the evolution direction. A balanced incentive and punishment mechanism for the investment and positive stimulus for workers can effectively promote both sides to take positive behaviors, and then realize good evolutionary stable situations. In addition, the initial perceptions of both sides have a decisive impact on the evolution direction. Strengthening communication with the mutual trust between both sides can improve safety performance of both sides. This study is valuable for contractors to design appropriate incentive and punishment measures and establish relevant strategies to promote safe behaviors of construction workers.
Keywords: construction workers; evolutionary game; incentive and penalty; mechanism design; unsafe behavior.
Copyright © 2022 Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Yuan and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An evolutionary game-theoretic analysis of construction workers' unsafe behavior: Considering incentive and risk loss.Front Public Health. 2022 Sep 13;10:991994. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.991994. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36176527 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary Process of Promoting Construction Safety Education to Avoid Construction Safety Accidents in China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 2;18(19):10392. doi: 10.3390/ijerph181910392. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34639703 Free PMC article.
-
Research on the Tournament Incentive Mechanism of the Safety Behavior for Construction Workers: Considering Multiple Heterogeneity.Front Psychol. 2021 Dec 13;12:796295. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.796295. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34966339 Free PMC article.
-
Analyzing Construction Workers' Unsafe Behaviors in Hoisting Operations of Prefabricated Buildings Using HAZOP.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 18;19(22):15275. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215275. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SEIR model and simulation research on unsafe psychological state propagation of construction workers considering safety climate and intimate relationships.Front Public Health. 2022 Oct 12;10:1031440. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1031440. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36311616 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An evolutionary game analysis of supervision behavior in public-private partnership projects: Insights from prospect theory and mental accounting.Front Psychol. 2023 Jan 11;13:1023945. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1023945. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36710850 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the effects of safety incentives on worker safety behavior control through image-based activity classification.Front Public Health. 2024 Aug 12;12:1430697. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1430697. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39188800 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cheng B., Fan C., Fu H., Huang J., Chen H., Luo X. (2022). Measuring and computing cognitive statuses of construction workers based on electroencephalogram: a critical review. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 22, 1–16. 10.1109/TCSS.2022.3158585 - DOI
-
- Fang D., Jiang Z., Zhang M., Wang H. (2015). An experimental method to study the effect of fatigue on construction workers' safe performance. Safe Sci. 73, 80–91. 10.1016/j.ssci.2014.11.019 - DOI
-
- Fang S., Ding S. (2009). The analysis of game theory in the safe problem of small coal mine. Operat. Res. Manage. Sci. 18, 73–78.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

