Enzootic bovine leukosis in a 21-month-old Japanese Black cow with high susceptibility
- PMID: 35686385
- PMCID: PMC9266502
- DOI: 10.1177/10406387221102123
Enzootic bovine leukosis in a 21-month-old Japanese Black cow with high susceptibility
Abstract
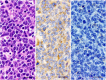
A 21-mo-old Japanese Black beef cow had swollen mandibular and superficial cervical lymph nodes. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of the superficial cervical lymph node revealed large lymphoblasts with mitoses present. The bovine leukemia virus (BLV) proviral load was relatively high, and phylogenetic analysis of the whole BLV genome classified the BLV strain as one with high viral replication activity. Genotyping of bovine leukocyte antigen genes indicated that the cow was susceptible to enzootic bovine leukosis (EBL). The bone morphogenetic protein 6 (BMP6) gene promoter region was hypermethylated. Monoclonal proliferation of B cells and monoclonal integration of the BLV provirus in the bovine genome were detected by a clonality test of B cells and an inverse PCR assay, respectively. At autopsy, generalized swelling of lymph nodes and spinal canal invasion by tumor tissue at vertebrae L5-6 were observed. Histologic analysis revealed diffuse proliferation of large round neoplastic cells that were positive for BLA36 and negative for CD3. The cow was definitively diagnosed with EBL based on these findings. Infection with a highly pathogenic strain of BLV, susceptibility of the BoLA-DRB3 alleles, and hypermethylation of the BMP6 gene may have contributed to the development of EBL in our case.
Keywords: BoLA; Japan; bovine leukemia virus; cattle; enzootic bovine leukosis; methylation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Angelos JA, Thurmond MC. Bovine lymphoma. In: Smith BP. ed. Large Animal Internal Medicine. 5th ed. Elsevier, 2015: 1070–1073.
-
- Baylin SB. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 2005;2(Suppl 1): S4–S11. - PubMed
-
- Divers TJ, Peek SF. The clinical examination. In: Peek SF, Divers TJ, eds. Rebhun’s Diseases of Dairy Cattle. 3rd ed. Elsevier, 2018:2–16.
-
- Florins A, et al. Emphasis on cell turnover in two hosts infected by bovine leukemia virus: a rationale for host susceptibility to disease. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2008;125:1–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

