An actin mechanostat ensures hyphal tip sharpness in Phytophthora infestans to achieve host penetration
- PMID: 35687685
- PMCID: PMC9187236
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abo0875
An actin mechanostat ensures hyphal tip sharpness in Phytophthora infestans to achieve host penetration
Abstract
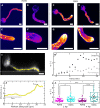
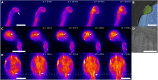
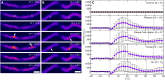
Filamentous plant pathogens apply mechanical forces to pierce their hosts surface and penetrate its tissues. Devastating Phytophthora pathogens harness a specialized form of invasive tip growth to slice through the plant surface, wielding their hypha as a microscopic knife. Slicing requires a sharp hyphal tip that is not blunted at the site of the mechanical interaction. How tip shape is controlled, however, is unknown. We uncover an actin-based mechanostat in Phytophthora infestans that controls tip sharpness during penetration. Mechanical stimulation of the hypha leads to the emergence of an aster-like actin configuration, which shows fast, local, and quantitative feedback to the local stress. We evidence that this functions as an adaptive mechanical scaffold that sharpens the invasive weapon and prevents it from blunting. The hyphal tip mechanostat enables the efficient conversion of turgor into localized invasive pressures that are required to achieve host penetration.
Figures
References
-
- P. V. Balhadère, N. J. Talbot, in Molecular Plant Pathology (CRC Press, ed. 1, 2020), pp. 1–25.
-
- Howard R. J., Valent B., Breaking and entering: Host penetration by the fungal rice blast pathogen Magnaporthe grisea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 50, 491–512 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Latijnhouwers M., de Wit P. J., Govers F., Oomycetes and fungi: Similar weaponry to attack plants. Trends Microbiol. 11, 462–469 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Rocha R. O., Elowsky C., Pham N. T., Wilson R. A., Spermine-mediated tight sealing of the Magnaporthe oryzae appressorial pore–rice leaf surface interface. Nat. Microbiol. 5, 1472–1480 (2020). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

