Discovery of 2-(furan-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide derivatives as novel inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease
- PMID: 35688005
- PMCID: PMC9162962
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114508
Discovery of 2-(furan-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide derivatives as novel inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Abstract
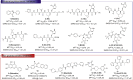
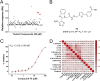
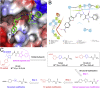
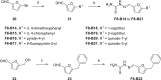
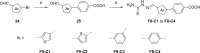
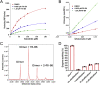
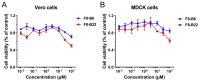
The COVID-19 posed a serious threat to human life and health, and SARS-CoV-2 Mpro has been considered as an attractive drug target for the treatment of COVID-19. Herein, we report 2-(furan-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide derivatives as novel inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro developed by in-house library screening and biological evaluation. Similarity search led to the identification of compound F8-S43 with the enzymatic IC50 value of 10.76 μM. Further structure-based drug design and synthetic optimization uncovered compounds F8-B6 and F8-B22 as novel non-peptidomimetic inhibitors of Mpro with IC50 values of 1.57 μM and 1.55 μM, respectively. Moreover, enzymatic kinetic assay and mass spectrometry demonstrated that F8-B6 was a reversible covalent inhibitor of Mpro. Besides, F8-B6 showed low cytotoxicity with CC50 values of more than 100 μM in Vero and MDCK cells. Overall, these novel SARS-CoV-2 Mpro non-peptidomimetic inhibitors provide a useful starting point for further structural optimization.
Keywords: 2-(furan-2-ylmethylene)hydrazine-1-carbothioamide derivatives; Main protease; Non-peptidomimetic inhibitors; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

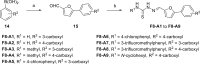

Similar articles
-
Computational Selectivity Assessment of Protease Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 19;22(4):2065. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042065. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669738 Free PMC article.
-
Iterated Virtual Screening-Assisted Antiviral and Enzyme Inhibition Assays Reveal the Discovery of Novel Promising Anti-SARS-CoV-2 with Dual Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 22;22(16):9057. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169057. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445763 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Evaluation of Andrographolide Analogues as SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors: Molecular Modeling and in vitro Studies.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 15;19:3907-3924. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S514193. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40391180 Free PMC article.
-
An Updated Review on SARS-CoV-2 Main Proteinase (MPro): Protein Structure and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(6):442-460. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666201207095117. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33292134 Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Mpro: A Potential Target for Peptidomimetics and Small-Molecule Inhibitors.Biomolecules. 2021 Apr 19;11(4):607. doi: 10.3390/biom11040607. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33921886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
X-ray Structures and Computational Studies of Two Bioactive 2-(Adamantane-1-carbonyl)-N-substituted Hydrazine-1-carbothioamides.Molecules. 2022 Dec 1;27(23):8425. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238425. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G.F., Tan W., China Novel Coronavirus I., Research T. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:727–733. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li G., De Clercq E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:149–150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

