The immune cell atlas of human neuroblastoma
- PMID: 35688160
- PMCID: PMC9245004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100657
The immune cell atlas of human neuroblastoma
Abstract
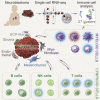
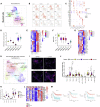
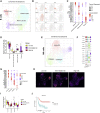
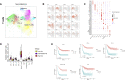
Understanding the complete immune cell composition of human neuroblastoma (NB) is crucial for the development of immunotherapeutics. Here, we perform single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) on 19 human NB samples coupled with multiplex immunohistochemistry, survival analysis, and comparison with normal fetal adrenal gland data. We provide a comprehensive immune cell landscape and characterize cell-state changes from normal tissue to NB. Our analysis reveals 27 immune cell subtypes, including distinct subpopulations of myeloid, NK, B, and T cells. Several different cell types demonstrate a survival benefit. In contrast to adult cancers and previous NB studies, we show an increase in inflammatory monocyte cell state when contrasting normal and tumor tissue, while no differences in cytotoxicity and exhaustion score for T cells, nor in Treg activity, are observed. Our receptor-ligand interaction analysis reveals a highly complex interactive network of the NB microenvironment from which we highlight several interactions that we suggest for future therapeutic studies.
Keywords: cancer; human; immune cell landscape; immuno-oncology; immunotherapy; neuroblastoma; pediatric cancer; prognosis; single-cell RNA sequencing; survival.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.V.K. serves on the Scientific Advisory Board to Celsius Therapeutics and Biomage and also consults for Altos Labs.
Figures


References
-
- Pinto N.R., Applebaum M.A., Volchenboum S.L., Matthay K.K., London W.B., Ambros P.F., Nakagawara A., Berthold F., Schleiermacher G., Park J.R., et al. Advances in risk classification and treatment strategies for neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015;33:3008–3017. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.59.4648. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

