Comparative chloroplast genomes and phylogenetic analyses of Pinellia
- PMID: 35689783
- PMCID: PMC9304046
- DOI: 10.1007/s11033-022-07617-5
Comparative chloroplast genomes and phylogenetic analyses of Pinellia
Abstract
Background: Pinellia Tenore (Araceae) is a genus of perennial herbaceous plants, all of which have medicinal value. The chloroplast (cp) genome data of Pinellia are scarce, and the phylogenetic relationship and gene evolution remain unclear.
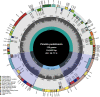
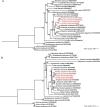
Methods and results: We sequenced and annotated the Pinellia pedatisecta cp genome and combined it with previously published genomes for other Pinellia species. We used bioinformatics methods to analyse the genomic structure, repetitive sequences, interspecific variation, divergence hotspots, phylogenetic relationships, divergence time estimation and selective pressure of four Pinellia plastomes. Results showed that the cp genomes of Pinellia varied in length between 168,178 (P. pedatisecta MN046890) and 164,013 bp (P. ternata KR270823). A total of 68-111 SSR loci were identified as candidate molecular markers for further genetic diversity study. Eight mutational hotspot regions were determined, including psbI-trnG-UCC, psbM-rpoB, ndhJ-trnT-UGU, trnP-UGG-trnW-CCA, ndhF-trnN-GUU, ndhG-ndhE, ycf1-rps15 and trnR-ycf1. Gene selection pressure suggested that four genes were subjected to positive selection. Phylogenetic inferences based on the complete cp genomes revealed a sister relationship between Pinellia and Arisaema plants whose divergence was estimated to occur around 22.48 million years ago. All Pinellia species formed a monophyletic evolutionary clade in which P. peltata, rather than P. pedatisecta, earlier diverged, indicating that P. pedatisecta is not the basal taxon of Pinellia but P. peltata may be.
Conclusions: The cp genomes of Pinellia will provide valuable information for species classification, identification, molecular breeding and evolutionary exploration of the genus Pinellia.
Keywords: Chloroplast genome; Divergence time estimation; Evolution; Phylogeny; Pinellia.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kozlov VA, Zhuravkin IN, Tsyrlova IG. Comparative analysis of the migratory capacity of hematopoietic stem cells and of immunocompetent precursors after acute hypoxia and the administration of testosterone. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1978;239(3):747–749. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 2021SACM-3/Research Incubation Fund Project of Shandong Academy of Chinese Medicine
- 2021-02/Major Special Project of Scientific and Technological Cooperation of Bijie City
- 202102041135/Medical and Health Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province
- 2020CXGC010505-04/Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

