The magnitude and timing of recalled immunity after breakthrough infection is shaped by SARS-CoV-2 variants
- PMID: 35690062
- PMCID: PMC9135796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.05.018
The magnitude and timing of recalled immunity after breakthrough infection is shaped by SARS-CoV-2 variants
Abstract
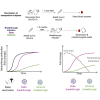
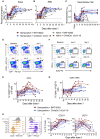
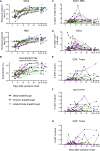
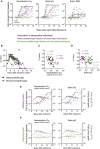
Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 protects from infection and improves clinical outcomes in breakthrough infections, likely reflecting residual vaccine-elicited immunity and recall of immunological memory. Here, we define the early kinetics of spike-specific humoral and cellular immunity after vaccination of seropositive individuals and after Delta or Omicron breakthrough infection in vaccinated individuals. Early longitudinal sampling revealed the timing and magnitude of recall, with the phenotypic activation of B cells preceding an increase in neutralizing antibody titers. While vaccination of seropositive individuals resulted in robust recall of humoral and T cell immunity, recall of vaccine-elicited responses was delayed and variable in magnitude during breakthrough infections and depended on the infecting variant of concern. While the delayed kinetics of immune recall provides a potential mechanism for the lack of early control of viral replication, the recall of antibodies coincided with viral clearance and likely underpins the protective effects of vaccination against severe COVID-19.
Keywords: B cell immunity; CD4 T cell immunity; CD8 T cell immunity; COVID-19 vaccines; Delta; Omicron; SARS-CoV-2; breakthrough infection; neutralizing antibodies; vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Backer J.A., Eggink D., Andeweg S.P., Veldhuijzen I.K., van Maarseveen N., Vermaas K., Vlaemynck B., Schepers R., van den Hof S., Reusken C.B., Wallinga J. Shorter serial intervals in SARS-CoV-2 cases with Omicron BA.1 variant compared with Delta variant, the Netherlands, 13 to 26 December 2021. Euro Surveill. 2022;27:2200042. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2022.27.6.2200042. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chan J.F., Yip C.C., To K.K., Tang T.H., Wong S.C., Leung K.H., Fung A.Y., Ng A.C., Zou Z., Tsoi H.W., et al. Improved molecular diagnosis of COVID-19 by the novel, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay validated in vitro and with clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020;58:e00310–e00320. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00310-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

