The combination of hydroxychloroquine and 2-deoxyglucose enhances apoptosis in breast cancer cells by blocking protective autophagy and sustaining endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 35690609
- PMCID: PMC9188615
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01074-6
The combination of hydroxychloroquine and 2-deoxyglucose enhances apoptosis in breast cancer cells by blocking protective autophagy and sustaining endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
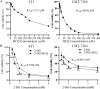
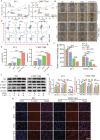
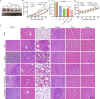
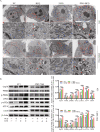
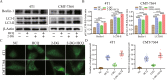
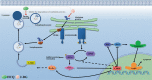
2-Deoxyglucose (2-DG) can be used in antitumour research by inhibiting glycolysis and promoting the endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) pathway, but its clinical application is restricted due to dose-limiting side effects and survival chance for cancer cells by protective autophagy. Therefore, our research explored whether the combination of hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), an FDA-approved autophagy inhibiting drug, and 2-DG is a promising therapeutic strategy. Here, we report that HCQ combined with 2-DG can further inhibit the viability and migration and induce apoptosis of breast tumour cells compared with other individual drugs. The combination of 2-DG and HCQ can significantly reduce transplanted tumour size and tumour cell metastasis of the lung and liver in vivo. At the cellular level, HCQ suppressed autolysosome formation and terminated the autophagy process induced by 2-DG-mediated ERS, resulting in the continuous accumulation of misfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, which generated sustained ERS through the PERK-eIF2α-ATF-4-CHOP axis and triggered the transformation from a survival process to cell death. Our research reinforced the research interest of metabolic disruptors in triple-negative breast cancer and emphasized the potential of the combination of 2-DG and HCQ as an anticancerous treatment.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Atiprimod triggered apoptotic cell death via acting on PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP and STAT3/NF-ΚB axis in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Jun;48(6):5233-5247. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06528-1. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34244887
-
2-Deoxyglucose and hydroxychloroquine HPLC-MS-MS analytical methods and pharmacokinetic interactions after oral co-administration in male rats.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Feb;12(1):e1173. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1173. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38294142 Free PMC article.
-
2-Deoxy-D-glucose has distinct and cell line-specific effects on the survival of different cancer cells upon antitumor drug treatment.FEBS J. 2018 Dec;285(24):4590-4601. doi: 10.1111/febs.14687. Epub 2018 Nov 17. FEBS J. 2018. PMID: 30375744
-
Chloroquine induces apoptosis in pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms via endoplasmic reticulum stress.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2020 Jul;27(7):431-439. doi: 10.1530/ERC-20-0028. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32369772
-
The Road of Solid Tumor Survival: From Drug-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Drug Resistance.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 13;8:620514. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.620514. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33928116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol in breast cancer treatment: from cellular effects to molecular mechanisms of action.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Oct 4;79(11):539. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04551-4. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36194371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Energy and endoplasmic reticulum stress induction by gold(III) dithiocarbamate and 2-deoxyglucose synergistically trigger cell death in breast cancer.J Biol Chem. 2024 Dec;300(12):107949. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107949. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 39481597 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium New Houttuyfonate Induces Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells via ROS/PDK1/AKT/GSK3β Axis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 6;15(5):1614. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051614. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900408 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Benzo(a)pyrene and Pyrene Exposure on Activating Autophagy and Correlation with Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Human Astrocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 18;26(4):1748. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041748. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40004212 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effects of 2-Deoxyglucose and Diclofenac Sodium on Breast Cancer Cells: A Comparative Evaluation of MDA-231 and MCF7 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 20;26(10):4894. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104894. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40430033 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 32172925/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

