Highly efficient engineered waste eggshell-fly ash for cadmium removal from aqueous solution
- PMID: 35690618
- PMCID: PMC9188607
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-13664-6
Highly efficient engineered waste eggshell-fly ash for cadmium removal from aqueous solution
Abstract
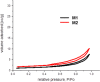
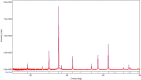
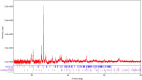
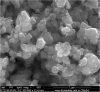
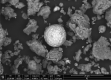
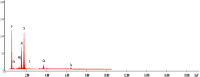
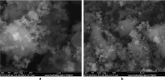
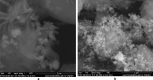
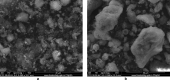
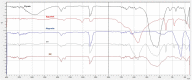
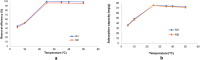
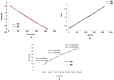
Sustainable waste and water management are key components of the newest EU policy regarding the circular economy. Simple, performant and inexpensive water treatment methods based on reusing waste are prerequisites for human health, sustainable development and environmental remediation. The design of performant, cost-effective absorbents represents a topical issue in wastewater treatment. This study aimed to investigate the development of a newly engineered adsorbent by functionalizing two different types of waste (industrial and food) with magnetic nanoparticles as environmentally friendly, highly efficient, cheap material for cadmium removal from aqueous solutions. This nano-engineered adsorbent (EFM) derived from waste eggshell and fly ash was used to remove the cadmium from the aqueous solution. SEM analysis has demonstrated that magnetite nanoparticles were successfully loaded with each waste. In addition, was obtained a double functionalization of the eggshell particles with ash and magnetite particles. As a result of this, the EFM surface area substantially increased, as confirmed by BET. A comprehensive characterization (BET, FT-IR, SEM, XRD and TGA) was performed to study the properties of this newly engineered adsorbent. Batch experiments were conducted to investigate the influence of different reaction parameters: temperature, pH, contact time, dosage adsorbent, initial concentration. Results showed that cadmium adsorption reached equilibrium in 120 min., at pH 6.5, for 0.25 g of adsorbent. The maximum efficiency was 99.9%. The adsorption isotherms research displayed that the Cd2+ adsorption fitted on the Freundlich model indicated a multi-molecular layer adsorption process. In addition, the thermodynamic study (ΔG < 0, ΔH > 0; ΔS > 0) shows that cadmium adsorption is a spontaneous and endothermic process. The adsorbent kinetic study was described with the pseudo-second-order model indicating a chemisorption mechanism. Desorption results showed that the nano-engineered adsorbent (EFM) can be reused. These data confirmed the possibility to enrich relevant theoretical knowledge in the field of waste recovery for obtaining newly designed adsorbents, performant and inexpensive for wastewater remediation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





















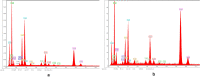

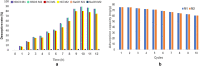
Similar articles
-
Possibility of removing cadmium pollution from the environment using a newly synthesized material coal fly ash.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Feb;27(5):4997-5008. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07163-x. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31845260
-
Rapid Removal of Toxic Remazol Brilliant Blue-R Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Juglans nigra Shell Biomass Activated Carbon as Potential Adsorbent: Optimization, Isotherm, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Investigation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12484. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012484. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293336 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of malachite green from wastewater using date seeds as natural adsorbent; isotherms, kinetics, Thermodynamic, and batch adsorption process design.Int J Phytoremediation. 2024 Jun;26(8):1321-1335. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2024.2316315. Epub 2024 Feb 26. Int J Phytoremediation. 2024. PMID: 38409765
-
A review on egg waste-based adsorbents for the removal of organic and inorganic contaminants from aqueous solution.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 24;11(3):e42278. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e42278. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39944350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein adsorption in three dimensions.Biomaterials. 2012 Feb;33(5):1201-37. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.059. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Biomaterials. 2012. PMID: 22088888 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Waste Eggshells as a Natural Filler for the Poly(Vinyl Chloride) Composites.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;14(20):4372. doi: 10.3390/polym14204372. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36297950 Free PMC article.
-
On the removal efficiency of copper ions in wastewater using calcined waste eggshells as natural adsorbents.Sci Rep. 2023 Jan 9;13(1):437. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-27682-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36624146 Free PMC article.
-
Wild grown Portulaca oleracea as a novel magnetite based carrier with in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxicity potential.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 13;15(1):8694. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92495-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40082491 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Waste Glass Particle Size on the Physico-Mechanical Properties and Porosity of Foamed Geopolymer Composites Based on Coal Fly Ash.Materials (Basel). 2023 Mar 1;16(5):2044. doi: 10.3390/ma16052044. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36903157 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Nanocomposites and Biopolymer-Based Nanocomposites for Hexavalent Chromium Removal from Aqueous Media.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Dec 12;16(24):3469. doi: 10.3390/polym16243469. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771321 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO (World Health Organization). Health through safe drinking water and basic sanitation. http://www.who.int/water_sanitation_health/mdg1/en/index.html (2008).
-
- Ghisellini P, Cialani C, Ulgiati S. A review on circular economy: The expected transition to a balanced interplay of environmental and economic systems. J. Clean Prod. 2016;114:11–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.09.007. - DOI
-
- Gautam RK, Sharma SK, Mahiya S. Chattopadhyaya Mahesh, C. Major contaminants in industrial and domestic wastewater a contamination of heavy metals in aquatic media: transport, toxicity and technologies for remediation. In: Sharma SK, editor. Heavy Metals in Water: Presence, Removal and Safety. The Royal Society of Chemistry; 2015.
-
- Mishra A, Tripathi BD. Utilization of fly ash in adsorption of heavy metals from wastewater. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2008;90(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1080/02772240801936786. - DOI
-
- Torres N, Gupta G. Use of fly ash in reducing toxicity of and heavy metals in wastewater effluent. J. Hazard. Mater. 1998;57(1–3):243–248.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

