Inclusion of a dual signal sequence enhances the immunogenicity of a novel viral vectored vaccine against the capsular group B meningococcus
- PMID: 35690803
- PMCID: PMC9187930
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-022-00809-3
Inclusion of a dual signal sequence enhances the immunogenicity of a novel viral vectored vaccine against the capsular group B meningococcus
Abstract
Background: Disease caused by the capsular group B meningococcus (MenB) is the leading cause of infectious death in UK infants. A novel adenovirus-based vaccine encoding the MenB factor H binding protein (fHbp) with an N-terminal dual signal sequence induces high titres of protective antibody after a single dose in mice. A panel of N-terminal signal sequence variants were created to assess the contribution of components of this sequence to transgene expression kinetics of the encoded antigen from mammalian cells and the resultant effect on immunogenicity of fHbp.
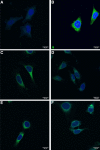
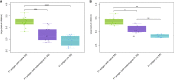
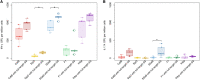
Results: The full-length signal sequence (FL SS) resulted in superior early antigen expression compared with the panel of variants, as measured by flow cytometry and confocal imaging, and supported higher bactericidal antibody levels against the expressed antigen in mouse sera < 6 weeks post-immunisation than the licensed four component MenB vaccine. The FL SS also significantly increased antigen-specific T cell responses against other adenovirus-encoded bacterial antigens in mice.
Conclusions: These findings demonstrate that the FL SS enhances immunogenicity of the encoded antigen, supporting its inclusion in other viral vectored bacterial antigen transgenes.
Keywords: Expression kinetics; Meningococcal disease; Signal sequence; Transgene; Viral vector vaccines.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.J.P. is Chair of UK Dept. Health and Social Care’s (DHSC) Joint Committee on Vaccination & Immunisation (JCVI) and is a member of the WHO’s SAGE. The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of DHSC, JCVI, NIHR or WHO. The University of Oxford has entered into a partnership with AstraZeneca on coronavirus vaccine development. C.S.R., C.D., D.S., and A.J.P. are named inventors on a patent application in the field of meningococcal vaccine. A.J.P waives all his rights to any patent.
Figures



References
-
- Finne J, et al. An IgG monoclonal antibody to group B meningococci cross-reacts with developmentally regulated polysialic acid units of glycoproteins in neural and extraneural tissues. J Immunol. 1987;138(12):4402–4407. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

