Identification of multiple isoforms of glucocorticoid receptor in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 35690807
- PMCID: PMC9188707
- DOI: 10.1186/s40463-022-00561-1
Identification of multiple isoforms of glucocorticoid receptor in nasal polyps of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
Abstract
Background: The conventional belief that glucocorticosteroid (GC) acts through a single brand glucocorticoid receptor (GR)α protein has changed dramatically with the discovery of multiple GR isoforms. We aimed to evaluate whether multiple GR protein isoforms are expressed in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and whether GR protein isoform expression profiles differ between different endotypes of CRSwNP.
Methods: Thirty-eight patients with CRSwNP and ten healthy volunteers were included. The protein expression of multiple GR isoforms in nasal polyps (NPs) tissue and control mucosae was examined by western blot analysis with different GR antibodies.
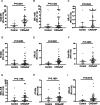
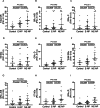
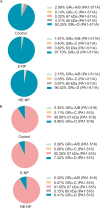
Results: Five bands, including three bands for known proteins (GRα-A/B, GRα-C, and GRα-D) and two bands for unidentified proteins at 67 kilodaltons (kDa) and 60 kDa, were identified with both total GR antibody (PA1-511A) and GRα-specific antibody (PA1-516). GRα-D intensity, which was abundant in nasal mucosa, was significantly increased in the CRSwNP group and was especially elevated in the noneosinophilic CRSwNP (NE-CRSwNP) group (PA1-511A: P < 0.001 and P = 0.0018; PA1-516: P < 0.003 and P = 0.006, respectively). Additionally, the intensities of the newly recognized 67 kDa and 60 kDa bands were much greater in the NE-CRSwNP subgroup than in the eosinophilic CRSwNP (E-CRSwNP) subgroup; in the E-CRSwNP subgroup, the median intensities were even lower than those in the control group.
Conclusions: This study provides evidence that nasal tissues express multiple GR protein isoforms. GR protein isoforms presented disease and tissue-specific expression profiles that differed between the CRSwNP and control groups and between the E-CRSwNP and NE-CRSwNP subgroups.
Keywords: Endotypes; Glucocorticoid receptor; Nasal polyps; Sinusitis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Saydy N, Moubayed SP, Bussières M, Janjua A, Kilty S, Lavigne F, et al. What is the optimal outcome after endoscopic sinus surgery in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis? A consultation of Canadian experts. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;50(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s40463-021-00519-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016YFC0905200/Key Technologies Research and Development Program
- 81970852and 82171110/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81630023/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82000962/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- IRT 13082/program for the Changjiang scholars and innovative research team
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

