Generation and characterization of genome-modified chondrocyte-like cells from the zebra finch cell line immortalized by c-MYC expression
- PMID: 35690812
- PMCID: PMC9188209
- DOI: 10.1186/s12983-022-00464-x
Generation and characterization of genome-modified chondrocyte-like cells from the zebra finch cell line immortalized by c-MYC expression
Abstract
Background: Due to their cost effectiveness, ease of use, and unlimited supply, immortalized cell lines are used in place of primary cells for a wide range of research purposes, including gene function studies, CRISPR-based gene editing, drug metabolism tests, and vaccine or therapeutic protein production. Although immortalized cell lines have been established for a range of animal species, there is still a need to develop such cell lines for wild species. The zebra finch, which is used widely as a model species to study the neurobiological basis of human speech disorders, has been employed in several functional studies involving gene knockdown or the introduction of exogenous transgenes in vivo; however, the lack of an immortalized zebra finch cell line has hampered precise genome editing studies.
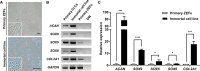
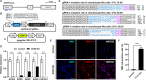
Results: Here, we established an immortalized cell line by a single genetic event, expression of the c-MYC oncogene, in zebra finch embryonic fibroblasts and examined its potential suitability for gene targeting investigations. Retroviral vector-mediated transduction of c-MYC was used to immortalize zebra finch primary fibroblasts; the transformed cells proliferated stably over several passages, resulting in the expression of chondrocyte-specific genes. The transfection efficiency of the immortalized cells was much higher than that of the primary cells. Targeted knockout of the SOX9 gene, which plays a role in the differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells into chondrocytes, was conducted in vitro and both apoptosis and decreased expression levels of chondrogenic marker genes were observed in edited cells.
Conclusions: The c-MYC induced immortalized chondrocyte-like cell line described here broadens the available options for establishing zebra finch cell lines, paves the way for in-depth biological researches, and provides convenient approaches for biotechnology studies, particularly genomic modification research.
Keywords: Chondrocyte-like cells; Gene editing; Immortalized cell line; Zebra finch; c-MYC.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Marino-Puertas L, Del Amo-Maestro L, Taules M, Gomis-Ruth FX, Goulas T. Recombinant production of human alpha2-macroglobulin variants and interaction studies with recombinant G-related alpha2-macroglobulin binding protein and latent transforming growth factor-beta2. Sci Rep. 2019;9:9186. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-45712-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

