Initial eGFR Changes with Ertugliflozin and Associations with Clinical Parameters: Analyses from the VERTIS CV Trial
- PMID: 35691283
- PMCID: PMC9501765
- DOI: 10.1159/000524889
Initial eGFR Changes with Ertugliflozin and Associations with Clinical Parameters: Analyses from the VERTIS CV Trial
Abstract
Introduction: Using data from the ertugliflozin cardiovascular outcomes trial in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (VERTIS CV; NCT01986881), associations between the initial estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) "dip" with eGFR slope, glucosuria/natriuresis-related measures, and safety were investigated.
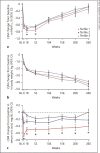
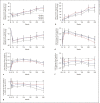
Methods: Patients were categorized into tertiles based on change in eGFR at week 6: >+1.00 mL/min/1.73 m2 (tertile 1), >-5.99 and ≤+1.00 (tertile 2), and ≤-6.00 (tertile 3). eGFR slope after week 6 and week 18 was assessed by tertile. Glucosuria/natriuresis-related measures were also determined. Adverse events (AEs) were analyzed in the acute (baseline-week 6) and chronic periods (week 6-30 days after last dose of trial medication).
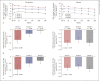
Results: In the ertugliflozin group, chronic eGFR slopes (95% CI, mL/min/1.73 m2/year; weeks 6-156) were -0.76 (-1.03, -0.50), -0.29 (-0.51, -0.07), and -0.05 (-0.26, 0.17) in tertiles 1, 2, and 3, respectively (p value <0.001), and approximately -1.5 mL/min/1.73 m2/year across tertiles in the placebo group (p value = 0.79). At week 18, least squares mean (LSM) changes from baseline in glycated hemoglobin (%) were -0.77, -0.71, and -0.67 in tertiles 1, 2, and 3, respectively, in the ertugliflozin group; a similar tertile-associated trend was observed for uric acid. At week 18, LSM changes from baseline in hematocrit (%) were 2.07, 2.33, and 2.55 in tertiles 1, 2, and 3, respectively, in the ertugliflozin group; similar tertile-associated trends were observed for blood pressure. All pinteraction values were <0.0001 for glucosuria- and natriuresis-related measures. Kidney-related AEs were reported more frequently in tertiles 3 and 2 in the chronic period for both placebo- and ertugliflozin-treated groups. In both periods and in all tertiles, incidences of AEs did not differ between placebo- and ertugliflozin-treated groups.
Conclusion: With ertugliflozin, the tertile with the largest initial dip in eGFR had a slower rate of chronic eGFR decline. Initial eGFR changes were associated with changes in both glucosuria- and natriuresis-related measures.
Keywords: Clinical trial; Diabetic nephropathy; Glomerular filtration rate; Kidney function decline; Kidney protection; Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
D.Z.I. Cherney has received consulting fees or speaking honoraria, or both, from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novo Nordisk, Mitsubishis-Tanabe, MAZE, Janssen, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim–Eli Lilly, AstraZeneca, Merck & Co., Inc., Prometic, and Sanofi, and has received operating funds from Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim–Eli Lilly, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, and Merck & Co., Inc. F. Cosentino has received fees from Abbott; AstraZeneca; Bayer; Boehringer Ingelheim; Bristol Myers Squibb; Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc, Rahway, NJ, USA; Novo Nordisk; and Pfizer, as well as research grants from Swedish Research Council, Swedish Heart & Lung Foundation, and the King Gustav V and Queen Victoria Foundation. S. Dagogo-Jack has led clinical trials for AstraZeneca, Novo Nordisk, Inc., and Boehringer Ingelheim, has received fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck & Co. Inc., and Sanofi, and holds equity interests in Jana care, Inc. and Aerami Therapeutics. D.K. McGuire has received honoraria for leadership roles in clinical trials for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eisai, Esperion, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Lexicon, Merck & Co., Inc., Novo Nordisk, CSL Behring, and Sanofi USA, and has received consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly USA, Merck & Co., Inc., Bayer, Pfizer, Novo Nordisk, Metavant, Afimmune, Lexicon, Applied Therapeutics, and Sanofi USA. R.E. Pratley has received the following (directed to his institution): speaker fees from Novo Nordisk; consulting fees from Merck, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sanofi, Scohia Pharma Inc., and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries; and grants from Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Hanmi Pharmaceuticals Co., Novo Nordisk, Poxel SA, and Sanofi. R. Frederich is an employee and shareholder of Pfizer Inc. M. Maldonado is an employee of MSD UK, who may own stock and/or stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. C.-C. Liu and A. Pong are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA, who may own stock and/or stock options in the Company. C.P. Cannon reports research grants and consulting fees from Pfizer Inc. and Merck & Co., Inc.; and research grants and consulting fees from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Janssen, research grants from Better Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, and Novo Nordisk, and consulting fees from Aegerion/Amryt, Alnylam, Amarin, Applied Therapeutics, Ascendia, Lexicon, Sanofi, Eli Lilly, and Rhoshan, and reports serving on the Data and Safety Monitoring Boards for the Veteran's Administration, Applied Therapeutics and NovoNordisk, outside the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The differential effects of ertugliflozin on glucosuria and natriuresis biomarkers: Prespecified analyses from VERTIS CV.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022 Jun;24(6):1114-1122. doi: 10.1111/dom.14677. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2022. PMID: 35233908 Clinical Trial.
-
Ertugliflozin and Slope of Chronic eGFR: Prespecified Analyses from the Randomized VERTIS CV Trial.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Sep;16(9):1345-1354. doi: 10.2215/CJN.01130121. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 34497110 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Glycemic efficacy and safety of the SGLT2 inhibitor ertugliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes and stage 3 chronic kidney disease: an analysis from the VERTIS CV randomized trial.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021 Oct;9(1):e002484. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2021-002484. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2021. PMID: 34620621 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A comprehensive review of the efficacy and safety of ertugliflozin.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2025 Apr;21(4):373-382. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2025.2457393. Epub 2025 Jan 23. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39838812 Review.
-
Ertugliflozin for treatment of patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Aug;11(8):747-753. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2018.1503051. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30025475 Review.
Cited by
-
Pleiotropic Effects of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 12;12(8):2824. doi: 10.3390/jcm12082824. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37109162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic Nephropathy: Update on Pillars of Therapy Slowing Progression.Diabetes Care. 2023 Sep 1;46(9):1574-1586. doi: 10.2337/dci23-0030. Diabetes Care. 2023. PMID: 37625003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abrupt Decline in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate after Initiating Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Predicts Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Mar;48(2):242-252. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2023.0201. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 38273790 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics.Diabetes Metab J. 2022 Jul;46(4):543-551. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0209. Epub 2022 Jul 27. Diabetes Metab J. 2022. PMID: 35929172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Kidney hemodynamic effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in diabetes: physiology and clinical implications.Clin Kidney J. 2024 Nov 27;18(1):sfae370. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfae370. eCollection 2025 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2024. PMID: 40008354 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cherney DZI, Perkins BA, Soleymanlou N, Maione M, Lai V, Lee A, et al. Renal hemodynamic effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Circulation. 2014 Feb 4;129((5)):587–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

