A weighted approach for spatio-temporal clustering of COVID-19 spread in Italy
- PMID: 35691657
- PMCID: PMC8949655
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sste.2022.100500
A weighted approach for spatio-temporal clustering of COVID-19 spread in Italy
Abstract
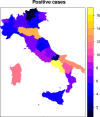
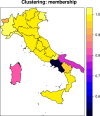
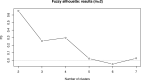
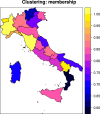
The SARS-Cov-2 has spread differently over space and time worldwide. By monitoring the contagion's time evolution, the November 3 2020 the Italian government introduced differentiated regime of restrictions among its regions. This experiment demonstrated that public health policies can be effectively designed by means of clustering. This paper proposes a fuzzy clustering model where spatial and temporal dimensions of the disease spread are optimally weighted. The resulting model is applied with the aim of identifying groups of Italian regions with similar contagion spread. We found that two groups of regions sharing similar patterns of COVID-19 spread over both space and time exist. Appropriate public health policies can be designed on the basis of this evidence.
Keywords: COVID-19; Fuzzy clustering; LISA; Policy design; Spatial auto-correlation; Time series.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Anselin L. Local indicators of spatial association—LISA. Geogr. Anal. 1995;27(2):93–115.
-
- Bastos J.A., Caiado J. On the classification of financial data with domain agnostic features. Internat. J. Approx. Reason. 2021;138:1–11.
-
- Bezdek J.C., Ehrlich R., Full W. FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 1984;10(2–3):191–203.
-
- Caiado J., Crato N., Peña D. A periodogram-based metric for time series classification. Comput. Statist. Data Anal. 2006;50(10):2668–2684.
-
- Campello R.J. A fuzzy extension of the rand index and other related indexes for clustering and classification assessment. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2007;28(7):833–841.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

