The impact of COVID-19 on soft contact lens wear in established European and US markets
- PMID: 35691828
- PMCID: PMC9125045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clae.2022.101718
The impact of COVID-19 on soft contact lens wear in established European and US markets
Abstract
Purpose: To characterise changes in soft contact lens wearing habits during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A detailed online questionnaire was circulated to individuals aged 40-70 years, during the period April to May 2021. Data sampling took place in the United Kingdom (UK), United States of America (USA), Netherlands, Germany, France, Spain and Italy. Only data pertaining to individuals who were soft contact lens wearers were included. Data were extracted for questions relating to contact lens wearing habits pre- and during the COVID-19 pandemic, and expectations for future lens wear beyond the pandemic.
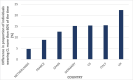
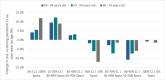
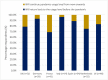
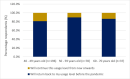
Results: Seven-hundred and twenty-eight individuals were identified as soft contact lens wearers of which six-hundred and nineteen wore a combination of contact lenses and spectacles. Most respondents indicated contact lens wear times had either remained the same (57.3%) or increased (9.8%) during the pandemic. The country with the greatest proportion of respondents decreasing wear time during COVID-19 was the UK (45.3%), and the least in the Netherlands (20.0%). The primary cause of decreased lens wear was attributed to leaving the home less often (70.0%), and the second most common reason due to concerns about hygiene (10.8%). Most respondents (83.9%), however, expressed a desire to return to pre-pandemic wear times once the pandemic was over.
Conclusions: Practitioner concerns about contact lens market recovery ought to be assuaged by the survey outcomes which show most individuals to have maintained lens wear during the pandemic. In view of the continued lens wear, as and when restrictions ease, ECPs may wish to encourage patients to return for routine check-ups that may have been missed due to the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Compliance; Contact lens; Pandemic; Patient preferences.
Copyright © 2022 British Contact Lens Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Neil Retallic is an employee of Menicon Co. Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Xu L, Ma Y, Yuan J, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang G, Tu C, Lu X, Li J, Xiong Y, Chen F, Liu X, Xue Z, Zhou M, Li WQ, Wu N, Bao J, Chen H, Lu F, Su J, Qu J; Myopic Epidemiology and Intervention Study. COVID-19 Quarantine Reveals That Behavioral Changes Have an Effect on Myopia Progression. Ophthalmology. 2021 Apr 14:S0161-6420(21)00257-8. 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.04.001. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 33857574. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

