Pathogenic associations between oral and gastrointestinal diseases
- PMID: 35691866
- PMCID: PMC9691515
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.05.006
Pathogenic associations between oral and gastrointestinal diseases
Abstract
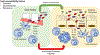
Both periodontitis and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) are complex chronic conditions characterized by aberrant host immune response and dysregulated microbiota. Emerging data show an association between periodontitis and IBD, including direct and indirect mechanistic links between oral and intestinal inflammation. Direct pathways include translocation of proinflammatory microbes from the oral cavity to the gut and immune priming. Indirect pathways involve systemic immune activation with possible nonspecific effects on the gut. There are limited data on the effects of periodontal disease treatment on IBD course and vice versa, but early reports suggest that treatment of periodontitis decreases systemic immune activation and that treatment of IBD is associated with periodontitis healing, underscoring the importance of recognizing and treating both conditions.
Keywords: immunology; inflammatory bowel disease; microbiome; oral–gut axis; pathobiont; periodontal disease.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

