Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 recombinant S-protein vaccine S-268019-b in cynomolgus monkeys
- PMID: 35691872
- PMCID: PMC9167832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.05.081
Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 recombinant S-protein vaccine S-268019-b in cynomolgus monkeys
Abstract
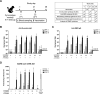
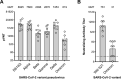
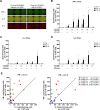
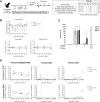
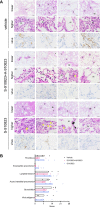
The vaccine S-268019-b is a severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike (S)-protein vaccine consisting of full-length recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S-protein (S-910823) as antigen, mixed with the squalene-based adjuvant A-910823. The current study evaluated the immunogenicity of S-268019-b using various doses of S-910823 and its vaccine efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 challenge in cynomolgus monkeys. The different doses of S-910823 combined with A-910823 were intramuscularly administered twice at a 3-week interval. Two weeks after the second dosing, dose-dependent humoral immune responses were observed with neutralizing antibody titers being comparable to that of human convalescent plasma. Pseudoviruses harboring S proteins from Beta and Gamma SARS-CoV-2 variants displayed approximately 3- to 4-fold reduced sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies induced after two vaccine doses compared with that against ancestral viruses, whereas neutralizing antibody titers were reduced >14-fold against the Omicron variant. Cellular immunity was also induced with a relative Th1 polarized response. No adverse clinical signs or weight loss associated with the vaccine were observed, suggesting safety of the vaccine in cynomolgus monkeys. Immunization with 10 µg of S-910823 with A-910823 demonstrated protective efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 challenge according to genomic and subgenomic viral RNA transcript levels in nasopharyngeal, throat, and rectal swab specimens. Pathological analysis revealed no detectable vaccine-dependent enhancement of disease in the lungs of challenged vaccinated monkeys. The current findings provide fundamental information regarding vaccine doses for human trials and support the development of S-268019-b as a safe and effective vaccine for controlling the current pandemic, as well as general protection against SARS-CoV-2 moving forward.
Keywords: Coronavirus disease 2019; Cynomolgus monkeys; Recombinant protein vaccine; S-268019-b; Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest MH, TH, HM, KD, NS, KY, TSo, and SO are employees of Shionogi & Co., Ltd. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19 - 12 October 2021 (https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...). Accessed October 17, 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

