Engaging Through Awareness: Purpose-Driven Framework Development to Evaluate and Develop Future Business Strategies With Exponential Technologies Toward Healthcare Democratization
- PMID: 35692334
- PMCID: PMC9174566
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.851380
Engaging Through Awareness: Purpose-Driven Framework Development to Evaluate and Develop Future Business Strategies With Exponential Technologies Toward Healthcare Democratization
Abstract
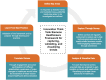
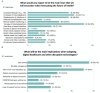
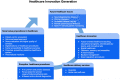
Industry 4.0 and digital transformation will likely come with an era of changes for most manufacturers and tech industries, and even healthcare delivery will likely be affected. A few trends are already foreseeable such as an increased number of patients, advanced technologies, different health-related business models, increased costs, revised ethics, and regulatory procedures. Moreover, cybersecurity, digital invoices, price transparency, improving patient experience, management of big data, and the need for a revised education are challenges in response to digital transformation. Indeed, forward-looking innovation about exponential technologies and their effect on healthcare is now gaining momentum. Thus, we developed a framework, followed by an online survey, to investigate key areas, analyze and visualize future-oriented developments concerning technologies and innovative business models while attempting to translate visions into a strategy toward healthcare democratization. When forecasting the future of health in a short and long-term perspective, results showed that digital healthcare, data management, electronics, and sensors were the most common predictions, followed by artificial intelligence in clinical diagnostic and in which hospitals and homes would be the places of primary care. Shifting from a reactive to a proactive digital ecosystem, the focus on prevention, quality, and faster care accessibility are the novel value propositions toward democratization and digitalization of patient-centered services. Longevity will translate into increased neurodegenerative, chronic diseases, and mental illnesses, becoming severe issues for a future healthcare setup. Besides, data privacy, big data management, and novel regulatory procedures were considered as potential problems resulting from digital transformation. However, a revised education is needed to address these issues while preparing future health professionals. The "P4 of health", a novel business model that is outcome-based oriented, awareness and acceptance of technologies to support public health, a different mindset that is proactive and future-oriented, and an interdisciplinary setting to merge clinical and technological advances would be key to a novel healthcare ecosystem. Lastly, based on the developed framework, we aim to conduct regular surveys to capture up-to-date technological trends, sustainable health-related business models, and interdependencies. The engagement of stakeholders through awareness and participation is the key to recognizing and improving healthcare needs and services.
Keywords: Industry 4.0; Innovation Think Tank; artificial intelligence; disruptive technologies; healthcare democratization; innovation; patient-centric; revised education.
Copyright © 2022 Barbazzeni, Haider and Friebe.
Conflict of interest statement
This study received funding from Siemens Healthineers. The funder had the following involvement with the study: study design, data collection, project supervision, revision of the manuscript, and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
A Structured Pathway Toward Disruption: A Novel HealthTec Innovation Design Curriculum With Entrepreneurship in Mind.Front Public Health. 2021 Sep 3;9:715768. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.715768. eCollection 2021. Front Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34540788 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the National Healthcare Ecosystem to Position Medical Affairs as a Strategic Element: Lessons Learned from AstraZeneca Spain.Pharmaceut Med. 2025 Jan;39(1):39-50. doi: 10.1007/s40290-024-00542-x. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Pharmaceut Med. 2025. PMID: 39715922 Free PMC article.
-
ASAS-NANP symposium: mathematical modeling in animal nutrition: limitations and potential next steps for modeling and modelers in the animal sciences.J Anim Sci. 2022 Jun 1;100(6):skac132. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac132. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35419602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Industrial Needs in the Fields of Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things and Edge Computing.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;22(12):4501. doi: 10.3390/s22124501. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Population Cancer Medicine in Cancer of the Uterine Cervix: A Potential Roadmap to Eradicate Cervical Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Feb 6;16(2):e53733. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53733. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38455773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of the current status and future vision of innovation in a tertiary hospital in Catalonia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Health Serv Res. 2025 Jul 18;25(1):958. doi: 10.1186/s12913-025-13009-9. BMC Health Serv Res. 2025. PMID: 40682027 Free PMC article.
-
Precision Population Cancer Medicine in Brain Tumors: A Potential Roadmap to Improve Outcomes and Strategize the Steps to Bring Interdisciplinary Interventions.Cureus. 2024 Oct 12;16(10):e71305. doi: 10.7759/cureus.71305. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39529768 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sneha S, Straub DW. E-Health: Value Proposition and Technologies Enabling Collaborative Healthcare. Honolulu, HI: HICSS; (2017). 10.24251/HICSS.2017.108 - DOI
-
- Chiasson M, Davidson E, Kaplan B, Kukafka R, Kuperman G. Strangers in a strange land: Can is meet the challenges and opportunities of research in healthcare. In: Proceedings of the Tenth Americas Conference in Information Systems. New York, NY; (2004).
-
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013–2020. World Health Organization (2013). Available online at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/94384 (accessed November 20, 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

