Automated Multi-View Multi-Modal Assessment of COVID-19 Patients Using Reciprocal Attention and Biomedical Transform
- PMID: 35692335
- PMCID: PMC9174692
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.886958
Automated Multi-View Multi-Modal Assessment of COVID-19 Patients Using Reciprocal Attention and Biomedical Transform
Abstract
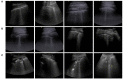
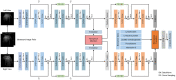
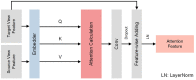
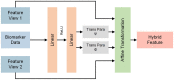
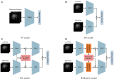
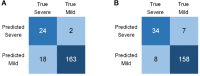
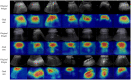
Automated severity assessment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients can help rationally allocate medical resources and improve patients' survival rates. The existing methods conduct severity assessment tasks mainly on a unitary modal and single view, which is appropriate to exclude potential interactive information. To tackle the problem, in this paper, we propose a multi-view multi-modal model to automatically assess the severity of COVID-19 patients based on deep learning. The proposed model receives multi-view ultrasound images and biomedical indices of patients and generates comprehensive features for assessment tasks. Also, we propose a reciprocal attention module to acquire the underlying interactions between multi-view ultrasound data. Moreover, we propose biomedical transform module to integrate biomedical data with ultrasound data to produce multi-modal features. The proposed model is trained and tested on compound datasets, and it yields 92.75% for accuracy and 80.95% for recall, which is the best performance compared to other state-of-the-art methods. Further ablation experiments and discussions conformably indicate the feasibility and advancement of the proposed model.
Keywords: COVID-19; computer aided diagnosis; deep learning; multi-modal; multi-view.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Zhao, Gan, Liu, Zou, Xu, Chen, Fan and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
XC was employed by BGI Research. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pre-gating and contextual attention gate - A new fusion method for multi-modal data tasks.Neural Netw. 2024 Nov;179:106553. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106553. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Neural Netw. 2024. PMID: 39053303
-
Intensive vision-guided network for radiology report generation.Phys Med Biol. 2024 Feb 5;69(4). doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad1995. Phys Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38157546
-
Pay attention to doctor-patient dialogues: Multi-modal knowledge graph attention image-text embedding for COVID-19 diagnosis.Inf Fusion. 2021 Nov;75:168-185. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.05.015. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Inf Fusion. 2021. PMID: 34093095 Free PMC article.
-
Judgment of benign and early malignant colorectal tumors from ultrasound images with deep multi-View fusion.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Mar;215:106634. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106634. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35081497
-
GACDN: generative adversarial feature completion and diagnosis network for COVID-19.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 21;21(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00681-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34674660 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Detection and Classification of Scaphoid Fractures in Radiograph by Using a Convolutional Neural Network.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 30;14(21):2425. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14212425. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518391 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

