Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Inflammation Diminishes Cross-Linked Collagen Structures in an Experimental Rabbit Model of Corneal Cross-Linking
- PMID: 35692541
- PMCID: PMC9178108
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.762730
Ovalbumin-Induced Allergic Inflammation Diminishes Cross-Linked Collagen Structures in an Experimental Rabbit Model of Corneal Cross-Linking
Abstract
Background: Allergic conjunctivitis (AC) is one of the reported potential risk factors of progression in keratoconus patients after corneal cross-linking surgery; however, the causal relationship is still inconclusive. Recent studies have indicated that various inflammatory cytokines play a vital role in the development of primary keratoconus. It is still unclear whether these inflammatory mediators also trigger CXL failures. This study aimed to investigate the impact of AC on the rabbit corneas after trans-epithelial corneal cross-linking (TCXL).
Methods: A total of six rabbits were kept untreated as the normal control (NC) group. A total of 18 rabbits were treated by TCXL and divided into three groups (six in each group), namely, no treatment (TCXL group); induction of AC (TCXL + AC group); and induction of AC plus topical prednisolone acetate (TCXL + AC + PA group), according to additional treatment. AC was induced by topical application of ovalbumin after intraperitoneal pre-sensitization with ovalbumin. Rabbits were evaluated by slit lamp, in vivo laser scanning confocal microscopy, anterior segment optical coherence tomography, and measurement of corneal biomechanics. The cornea specimens were collected for the transmission electron microscope, the collagenase I digestion test, and PCR assay for TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), lysyl oxidase (LOX), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) on the day (D) 28.
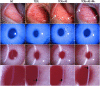
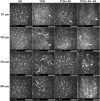
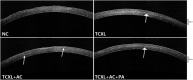
Results: On D28, the TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, MMP-9, and LOX levels were significantly increased while the TIMP-1 was decreased in the TCXL + AC group when compared with the TCXL and TCXL + AC + PA groups. In vivo confocal microscopy revealed that at a depth of 150-210 μm, a trabecular patterned hyperdense structure surrounded by elongated needle-like processes could be observed in the TCXL and TCXL + AC + PA groups, but hardly seen in the TCXL + AC group. The demarcation lines were indistinct and blurred in the TCXL + AC group. An electron microscope demonstrated less interlacing fibril lamellae and higher interfibrillar spacing in the TCXL + AC group. The stability of corneal biomechanics and resistance to collagenase were decreased in the TCXL + AC group.
Conclusion: The corneal microstructures induced by TCXL and biomechanical stability were diminished in rabbits with AC but could be maintained by topical anti-inflammatory treatment. Our results supported the causal relationship between altered cytokine profiles and corneal microstructure after primary corneal cross-linking.
Keywords: allergic conjunctivitis; corneal collagen cross-linking; in vivo confocal microscopy (IVCM); inflammatory cytokine; matrix metalloproteinase.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao, Liang, He, Wang, Zhu, Li, Liu, Zong, Jin, Wu, Li and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

