Natural products' role against COVID-19
- PMID: 35693131
- PMCID: PMC9122563
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03774e
Natural products' role against COVID-19
Abstract
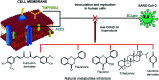
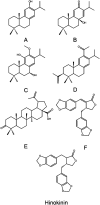
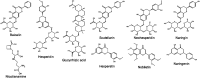
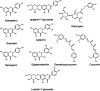
COVID-19 is a viral disease caused by a new severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS-CoV-2), which has quickly resulted in a pandemic. As a great threat to global public health, the development of a treatment has become vital, and a rush to find a cure has mobilized researchers from all areas across the world. Synthetic drugs, such as hydroxychloroquine, have gained attention. However, the efficacy of repositioned drugs is still under evaluation, and besides, some severe side effects are a cause for concern. This emphasizes the urgency for treatment options, which can be both safe and effective. With this in mind, natural products could be an important resource in the development of COVID-19 treatment, as they have already contributed in the past to treatments against other viruses, such as HIV, MERS-CoV, and influenza. Natural products are described long term as bioactive substances and some phytochemical classes such as flavonoids, alkaloids, and peptides are known antiviral bioproducts, and have been virtually tested with success against COVID-19. However, important issues still need to be addressed as to their bioavailability and true efficacy in vivo. This review intends to systematically evaluate the natural metabolites that could potentially be used against this new disease looking at their natural sources, mechanism of action and previous pharmacological usages. The aim is to provide a starting point for this research area in order to speed up the establishment of anti-SARS-CoV-2 bioproducts.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Hussain W. Haleem K. S. Khan I. Tauseef I. Qayyum S. Ahmed B. Riaz M. N. Future Virol. 2017;12:299–308. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2016-0110. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

