Mental Arithmetic Task Recognition Using Effective Connectivity and Hierarchical Feature Selection From EEG Signals
- PMID: 35693148
- PMCID: PMC9168814
- DOI: 10.32598/bcn.2021.2034.1
Mental Arithmetic Task Recognition Using Effective Connectivity and Hierarchical Feature Selection From EEG Signals
Abstract
Introduction: Mental arithmetic analysis based on Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals can help understand disorders, such as attention-deficit hyperactivity, dyscalculia, or autism spectrum disorder where the difficulty in learning or understanding the arithmetic exists. Most mental arithmetic recognition systems rely on features of a single channel of EEG; however, the relationships between EEG channels in the form of effective brain connectivity analysis can contain valuable information. This study aims to find distinctive, effective brain connectivity features and create a hierarchical feature selection for effectively classifying mental arithmetic and baseline tasks.
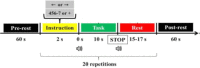
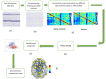
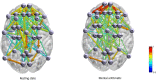
Methods: We estimated effective connectivity using Directed Transfer Function (DTF), direct DTF (dDTF) and Generalized Partial Directed Coherence (GPDC) methods. These measures determine the causal relationship between different brain areas. A hierarchical feature subset selection method selects the most significant effective connectivity features. Initially, Kruskal- Wallis test was performed. Consequently, five feature selection algorithms, namely, Support Vector Machine (SVM) method based on Recursive Feature Elimination, Fisher score, mutual information, minimum Redundancy Maximum Relevance (RMR), and concave minimization and SVM are used to select the best discriminative features. Finally, the SVM method was used for classification.
Results: The obtained results indicated that the best EEG classification performance in 29 participants and 60 trials is obtained using GPDC and feature selection via concave minimization method in Beta2 (15-22Hz) frequency band with 89% accuracy.
Conclusion: This new hierarchical automated system could be helpful in the discrimination of mental arithmetic and baseline tasks from EEG signals effectively.
Highlights: Propose effective connectivity to describe EEG signals during mental arithmetic task.Most significant connectivity features from generalized partial directed coherence method.Hierarchical feature selection from Kruskal-Wallis test and concave minimization method.
Plain language summary: Brain analysis methods by Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals provide a suitable method to monitor human brain activity due to having high temporal resolution, being noninvasive, inexpensive, and portable method. Analysis of mental arithmetic based EEG signal is helpful for psychological disorders like dyscalculia where they have learning understanding arithmetic, attention deficit hyperactivity, and autism spectrum disorders with attention deficit problem. This study finds distinctive effective brain connectivity features and creates a hierarchical feature selection for classification of mental arithmetic and baseline tasks effectively. Best EEG classification performance in 29 participants and 60 trials is obtained using Generalized Partial Directed Coherence (GPDC) methods and feature selection via concave minimization method in Beta2 (15-22Hz) frequency band with 89% accuracy. Thus, this new hierarchical automated system is useful for discrimination of mental arithmetic and baseline tasks from EEG signal effectively.
Keywords: Effective connectivity; Electroencephalogram (EEG); Feature selection; Mental arithmetic.
Copyright© 2021 Iranian Neuroscience Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Baccalá L. A., Sameshima K., Takahashi D. Y. (2007). Generalized partial directed coherence in digital signal processing. International Conference on Digital Signal Processing,163–66. [DOI: 10.1109/ICDSP.2007.4288544] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
