Unpacking the Emotional Experiences of Learners in a Blended Learning Context
- PMID: 35693530
- PMCID: PMC9174991
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.879696
Unpacking the Emotional Experiences of Learners in a Blended Learning Context
Abstract
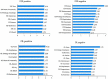
Understanding the relationship between emotion and learning behavior is conducive to learners' well-being and effective learning. However, previous studies only regarded emotion as an additional variable, and there lacked specific research on academic emotion in the blended learning (BL) context. BL is characterized by systematic integration of online and face-to-face (F2F) learning, hence leading to special emotional experiences. What is the emotional experience of learners in online learning? What is it like face-to-face? Does the connection between the two have an impact on learners' emotional experience? In order to address these questions and explore the emotional profiles of learners in BL context, this study constructs a typical BL context in a Chinese university, and conducts questionnaire and focus group interviews with 89 participants at the end of the semester. Data analysis showed that learners' emotions of face-to-face classes are more intense than those of online learning, both positive and negative. As to positive emotions, paired-sample t-test shows that mean values of feeling of challenge, comfort, sense of community, satisfaction, enthusiasm and interest in F2F are significantly higher than those of online learning. About negative emotions, stress, embarrassment, tension and frustration of F2F are significantly stronger than those of online learning, while boredom and disappointment of online learning are more intense than those for F2F section. Theme analysis identified 11 influencing factors of academic emotions, among which degree of difficulty, readiness before class, workload, and interaction are unique to BL and deserve special attention. These findings help form a picture of learners' academic emotions in BL context. It also provides practical reference for BL course design, so as to inspire emotions which are conducive to effective and in-depth learning.
Keywords: academic emotion; blended learning; negative emotion; positive emotion; valence.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alammary A., Sheard J., Carbone A. (2014). Blended learning in higher education: three different design approaches. Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 30 440–454. 10.14742/ajet.693 - DOI
-
- Arnold J. (ed.). (1999). Affect in Language Learning. Stuttgart: Ernst Klett Sprachen.
-
- Bock G. W., Zmud R. W., Kim Y., Lee J. (2005). Behavioral intention formation knowledge sharing: examining roles of extrinsic motivators, social-psychological forces, and organizational climate. MIS Q. 29 87–111. 10.2307/25148669 - DOI
-
- Cheng M. T., Huang W. Y., Hsu M. E. (2020). Does emotion matter? An investigation into the relationship between emotions and science learning outcomes in a game-based learning environment. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 51 2233–2251. 10.1111/bjet.12896 - DOI
-
- Cleveland-Innes M., Campbell P. (2012). Emotional presence, learning, and the online learning environment. Int. Rev. Res. Open Distrib. Learn. 13 269–292. 10.19173/irrodl.v13i4.1234 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials