Cranial morphology of the orectolobiform shark, Chiloscyllium punctatum Müller & Henle, 1838
- PMID: 35693755
- PMCID: PMC7612840
- DOI: 10.3897/vz.72.e84732
Cranial morphology of the orectolobiform shark, Chiloscyllium punctatum Müller & Henle, 1838
Abstract
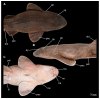
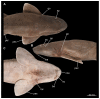
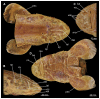
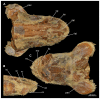
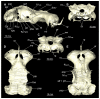
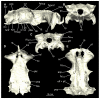
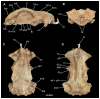
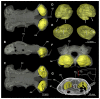
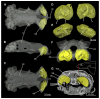
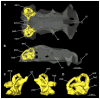
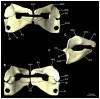
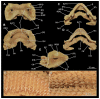
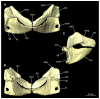
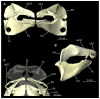
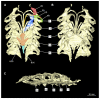
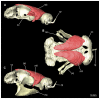
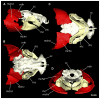
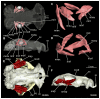
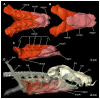
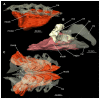
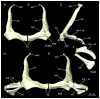
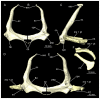
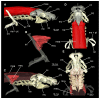
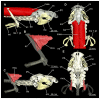
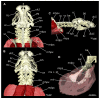
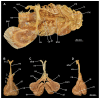
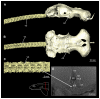
Elasmobranchs, comprising sharks, skates, and rays, have a long evolutionary history extending back into the Palaeozoic. They are characterized by various unique traits including a predominantly cartilaginous skeleton, superficial prismatic phosphatic layer, and permanent tooth replacement. Moreover, they exhibit a more or less marked sexual dimorphism. Especially the morphology of the chondrocranium and the elements of the whole cranial region of extant and extinct chondrichthyans can provide valuable information about corresponding functions, e.g. the feeding apparatus might reflect the diet of the animals. However, studies on sexual dimorphisms are lacking in orectolobiform sharks, therefore, little is known about possible sexual dimorphic characters in the cranial region in this group. For this reason, we present in this study a comprehensive morphological description of the cranial region of the brownbanded bamboo shark Chiloscyllium punctatum Müller & Henle, 1838, with a special focus on its sexual dimorphic characters. Our results reveal clear morphological differences in both sexes of the examined C. punctatum specimens, particularly in the chondrocranium and the mandibular arch. The female specimen shows a comparatively more robust and compact morphology of the chondrocranium. This pattern is also evident in the mandibular arch, especially in the palatoquadrate. The present study is the first to describe the morphology of an orectolobiform shark species in detail using both manual dissection and micro-CT data. The resulting data furthermore provide a starting point for pending studies and are intended to be a first step in a series of comparative studies on the morphology of the cranial region of orectolobiform sharks, including the determination of possible sexual dimorphic characteristics.
Keywords: Chiloscyllidae; Chondrichthyes; Galeomorphii; dissection; micro-CT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
























References
-
- Chen W-K, Liu K-M. Reproductive biology of whitespotted bamboo shark Chiloscyllium plagiosum in northern waters off Taiwan. Fisheries Science. 2006;72(6):1215–1224. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-2906.2006.01279.x. - DOI
-
- Compagno L. Interrelationships of living Elasmobranchii. Zool J Linne Soc. 1973;53:15.
-
- Compagno L. FAO species catalogue Vol 4 Sharks of the world An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date Part 1 Hexanchiformes to Lamniformes. FAO Fish Synop. 1984;125:1–249.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
