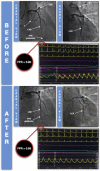
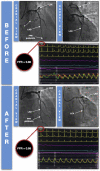
Transcatheter Occlusion of Coronary-Pulmonary Fistula With a Liquid Embolic Agent After Evaluation by FFR
- PMID: 35693909
- PMCID: PMC9175142
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaccas.2021.11.010
Transcatheter Occlusion of Coronary-Pulmonary Fistula With a Liquid Embolic Agent After Evaluation by FFR
Abstract
A 58-year-old man was admitted for stable angina. The coronary angiogram revealed a coronary-pulmonary fistula with a nonsignificant atheroma. We decided to perform percutaneous embolization of the fistula in view of the symptoms and the hemodynamic assessment findings. Embolization was performed using a liquid embolic agent with no residual flow. (Level of Difficulty: Intermediate.).
Keywords: CAF, coronary artery fistula; CPAF, coronary-pulmonary artery fistula; FFR, fractional flow reserve; LAD, left anterior descending (coronary artery); LEA, liquid embolic agent; coronary artery fistula; fractional flow reserve; liquid embolic agent.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have reported that they have no relationships relevant to the contents of this paper to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Vavuranakis M., Bush C.A., Boudoulas H. Coronary artery fistulas in adults: incidence, angiographic characteristics, natural history. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn. 1995;35:116–120. - PubMed
-
- Latson L.A. Coronary artery fistulas: how to manage them. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2007;70:110–116. - PubMed
-
- Said S.A., van der Werf T. Dutch survey of coronary artery fistulas in adults: congenital solitary fistulas. Int J Cardiol. 2006;106:323–332. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources