Editorial: Sensory Ecology of Phenotypic Plasticity: From Receptors via Modulators to Effectors
- PMID: 35694185
- PMCID: PMC9178266
- DOI: 10.3389/fnint.2022.930390
Editorial: Sensory Ecology of Phenotypic Plasticity: From Receptors via Modulators to Effectors
Keywords: anthropogenic impact; behavior; chemical cue; neuronal pathway; phenotypic plasticity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
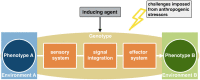
Comment on
- Editorial on the Research Topic Sensory Ecology of Phenotypic Plasticity: From Receptors via Modulators to Effectors
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

