Cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: a review
- PMID: 35694771
- PMCID: PMC9848325
- DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2022.2083977
Cerebral toxoplasmosis in HIV-infected patients: a review
Abstract
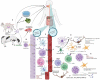
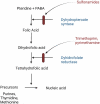
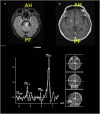
Toxoplasma gondii infection in the central nervous system commonly occurs among immunodeficient patients. Its prevalence is high in countries with a high burden of HIV and low coverage of antiretroviral drugs. The brain is one of the predilections for T. gondii infection due to its low inflammatory reaction, and cerebral toxoplasmosis occurs solely due to the reactivation of a latent infection rather than a new infection. Several immune elements have recently been recognized to have an essential role in the immunopathogenesis of cerebral toxoplasmosis. Although real-time isothermal amplification, next-generation sequencing, and enzyme-linked aptamer assays from blood samples have been the recommended diagnostic tools in some in-vivo studies, a combination of clinical symptoms, serology examination, and neuroimaging are still the daily standard for the presumptive diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis and early anti-toxoplasma administration. Clinical trials are needed to find a new therapy that is less likely to affect folate synthesis, have neuroprotective properties, or cure the latent phase of infection. The development of a vaccine is being extensively tested in animals, but its efficacy and safety for humans are still not proven.
Keywords: Brain; Toxoplasma gondii; human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); myelotoxicity; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Safarpour H, Cevik M, Zarean M, et al. Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection and associated risk factors in people living with HIV. AIDS. 2020;34(3):469–474. - PubMed
-
- CDC . Global health, division of parasitic diseases and malaria. Accessed 1 April 2021. https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/toxoplasmosis/epi.html
-
- Wang ZD, Wang SC, Liu HH, et al. Prevalence and burden of Toxoplasma gondii infection in HIV-infected people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet HIV. 2017;4(4):e177–e188. - PubMed
-
- WHO . AIDS epidemic update. USAIDS; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
